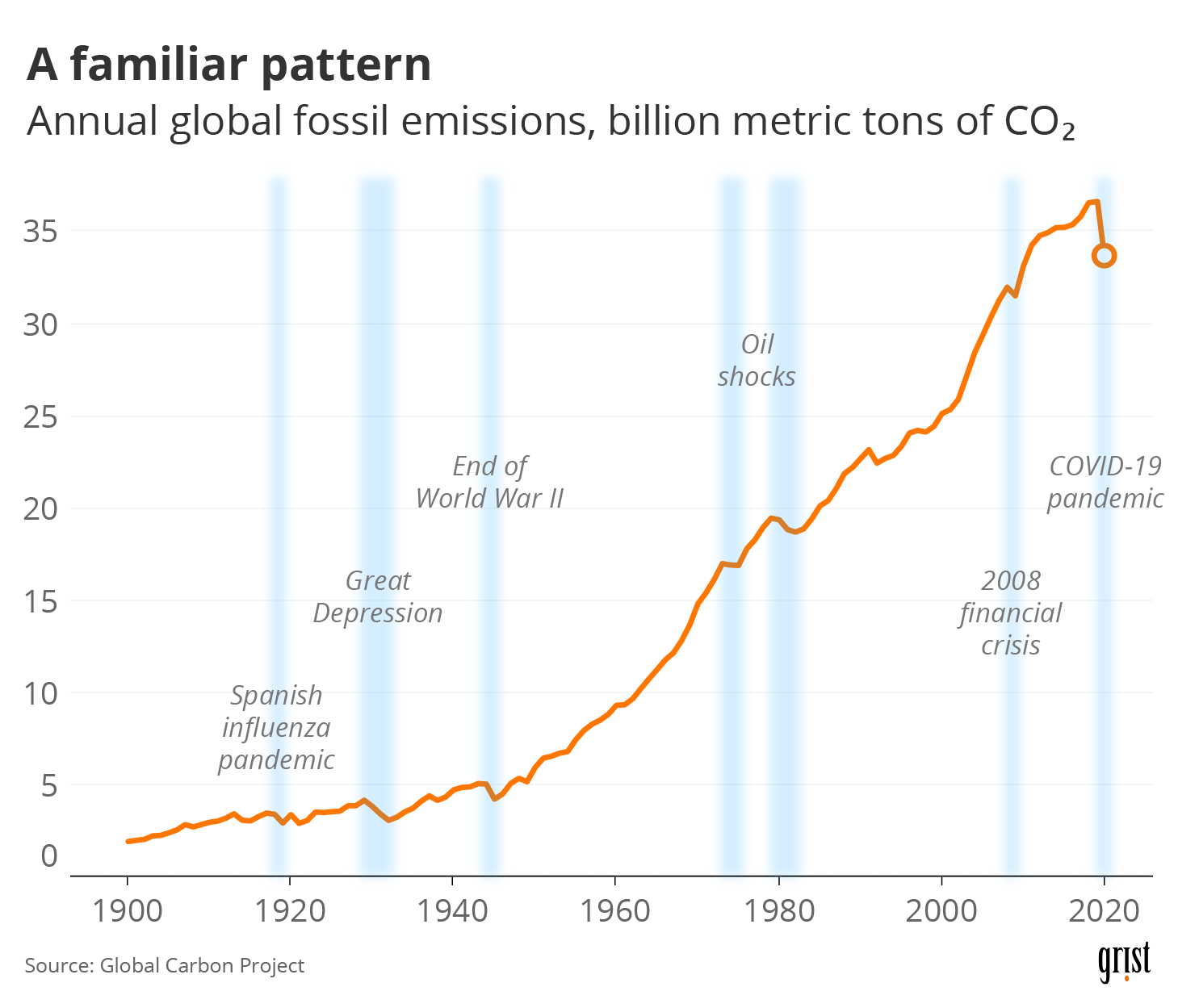
Greenhouse gas emissions in the United States dropped by an estimated 103% over the course of compared to the previous year, according to an analysis by the research firm Rhodium Group The decline was driven by COVID19related economic disruptions Emissions from various sectors including transportation, energy generation, industry, andThe pandemic will cause a dip in emissions, but this will only be temporary without a dramatic and planned shift to lowcarbon economies In 19, total greenhouse gas emissions, including landuse change, reached a new high of 591 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (GtCO 2 e) This means that atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide continue to grow, asThis can be used to express a tonne of a greenhousegas emitted in CO 2 equivalent terms, in order to provide a single measure of total greenhousegas emissions (in CO 2eq) The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has indicated a GWP for methane between 8487 when considering its impact over a year timeframe (GWP ) and between 26 when
After A Century Of Growth Have Carbon Emissions Reached Their Peak Grist
World greenhouse gas emissions 2020
World greenhouse gas emissions 2020-Despite a dip in greenhouse gas emissions from the COVID19 economic slowdown, the world is still heading for a catastrophic temperature rise above 3°C this century – far beyond the goals of the Paris Agreement But UNEP's Emissions Gap points to hope in a green pandemic recovery and growing commitments to netzero emissionsThis interactive chart shows annual greenhouse gas emissions – the amount a given country produces each year – across the world Again, this is measured in tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalents As is the case with CO 2 emissions, China is the world's largest emitter of greenhouse gases today It emits around twice as much



Sector By Sector Where Do Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Our World In Data
Raising livestock contributes significantly to carbon emissions, with animal agriculture accounting for 145% of the world's greenhouse gas emissions Scientific reports have Most of the world's greenhouse gas emissions come from a relatively small number of countries China, the United States, and the nations that make up the European Union are the three largest emitters on an absolute basis Per capita greenhouse gas emissions are highest in the United States and Russia Global Carbon Dioxide Emissions, 1850–40 Notes Note 4 February Final UK greenhouse gas emissions national statistics 1990 to 18 added 5 February 19 Final UK greenhouse gas emissions national statistics added 6 February 18
The AGGI in was 147, which means that we've turned up the warming influence from greenhouse gases by 47% since 1990; This article is more than 8 months old US greenhouse gas emissions fell 10% in as Covid curbed travel This article is more than 8 months old Transportation is currently the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions in the US, having surpassed electricity generation in 16 Emissions are produced through the burning of petroleum in
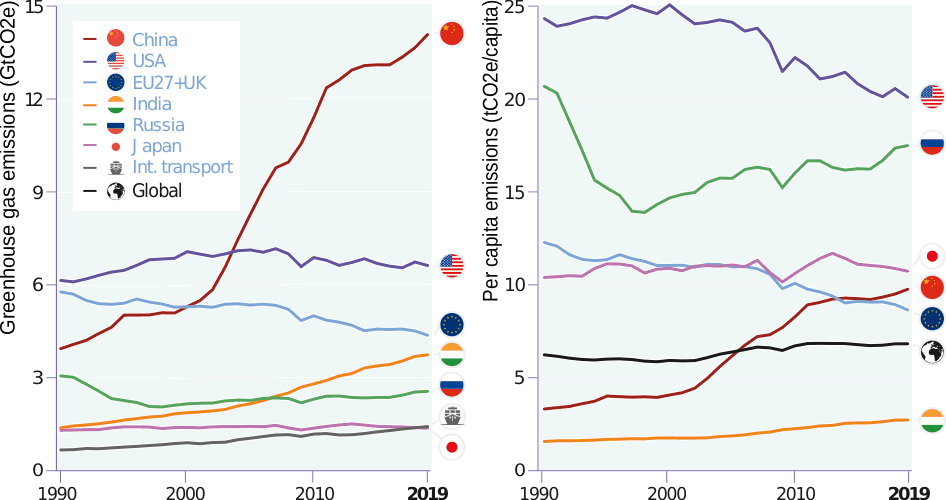
And what is driving emissions across the world In the navigation menu you also find In , greenhouse gas emissions decreased specifically by 179% compared to 19 This means that, after the decreases already registered in 18 and 19, global emissions reached a reduction of 11% compared to the base or reference year (1990) and 42% compared to 05 These are data from a report prepared by the Sustainability Observatory Led by theThe United States produced 66 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 19, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per personIn 19 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GhG, followed by the United States with 11%,



3



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Used Cait As Data Source Climatechange
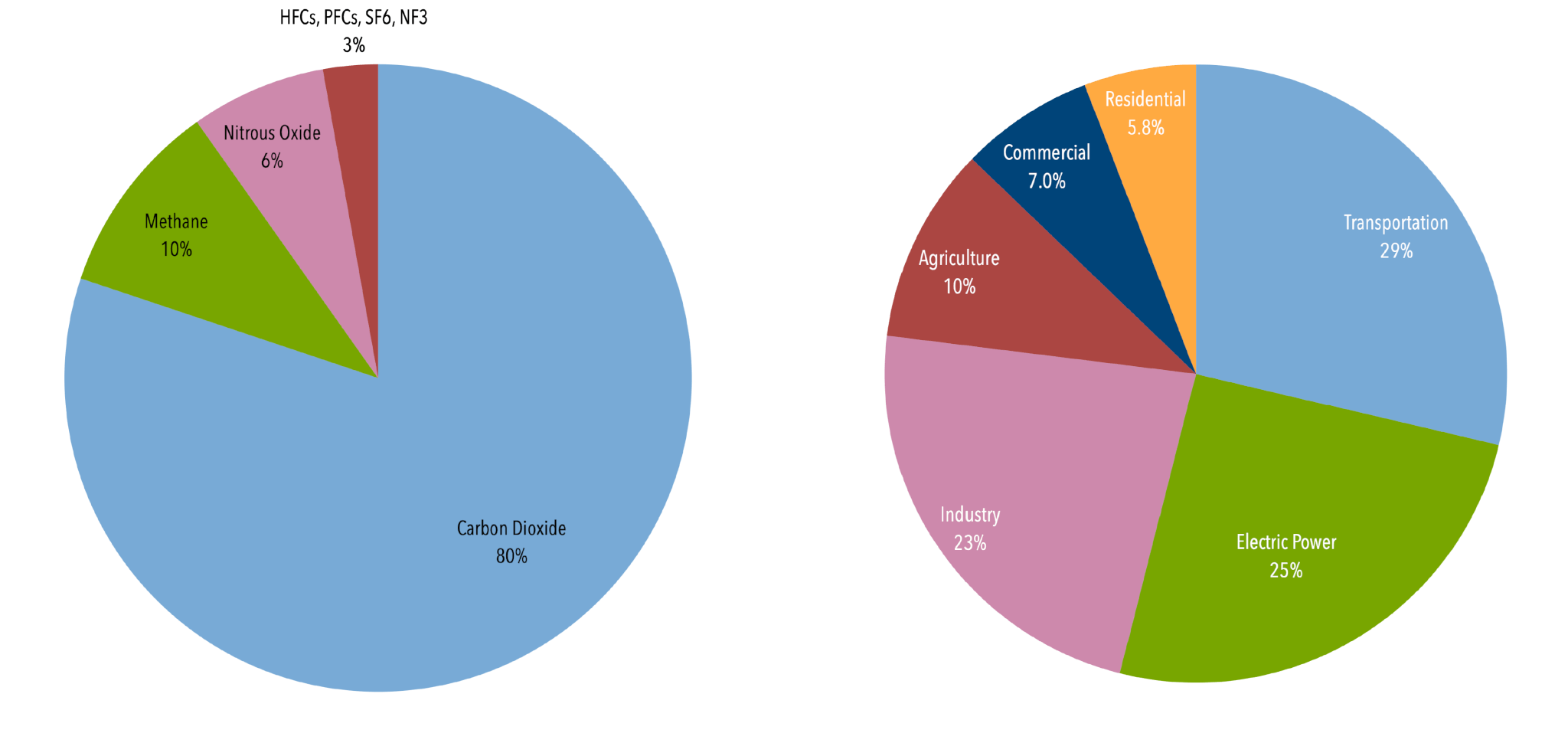
Greenhouse gas emissions by China are the largest of any country in the world both in production and consumption terms, and stem mainly from coal burning in China, including coalfired power stations, coal mining, and blast furnaces producing iron and steel When measuring productionbased emissions, China emitted over 12 gigatonnes CO 2eq of greenhouse gases in 14; Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activitiesIn 19, CO 2 accounted for about 80 percent of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals)The UN Environment Programme said that even if nations meet their current emissions reduction pledges, carbon emissions in will be eight to 12 gigatonnes above the level required to avoid a costly nosedive in greenhouse gas output The Emissions Gap Report 13, which was compiled by 44 scientific groups in 17 countries, warns that if the



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector




After A Century Of Growth Have Carbon Emissions Reached Their Peak Grist
The world's countries emit vastly different amounts of heattrapping gases into the atmosphere The chart above and table below both show data compiled by the International Energy Agency, which estimates carbon dioxide (CO 2) emissions from the combustion of coal, natural gas, oil, and other fuels, including industrial waste and nonrenewable municipal wasteHow do greenhouse gas emissions vary across the world?This page is just one in our collection of work on CO 2 and Greenhouse Gas Emissions The rest can be explored via the navigation menu at the top of this page There you can explore emissions of other greenhouse gases;



Metlink Royal Meteorological Society Country By Country Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gas Emission Levels Continued To Rise In 16 Pbl Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency
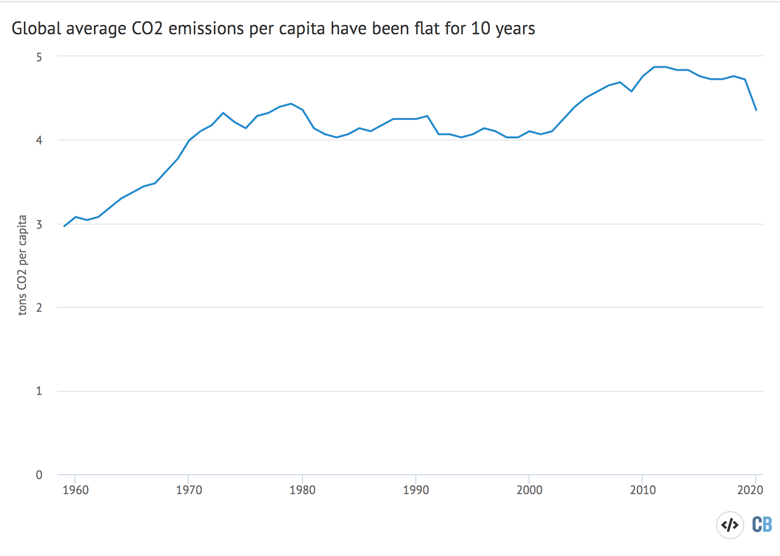
It took ~240 years for the AGGI to go from 0 to 1, ie, to reach 100%, and 30 years for it to increase by another 47% In terms of CO 2 equivalents, the atmosphere in contained 504 ppm, of which 412 is CO 2 alone The rest comes from otherHuman emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases – are a primary driver of climate change – and present one of the world's most pressing challenges 1 This link between global temperatures and greenhouse gas concentrations – especially CO 2 – has been true throughout Earth's history 2 To set the scene, let's look at how the planet has warmedGreenhouse gas emissions are greenhouse gases vented to the Earth's atmosphere because of humans the greenhouse effect of their 50 billion tons a year causes climate change Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels coal, oil, and natural gas The largest polluters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many stateowned by OPEC and Russia Human



U S Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



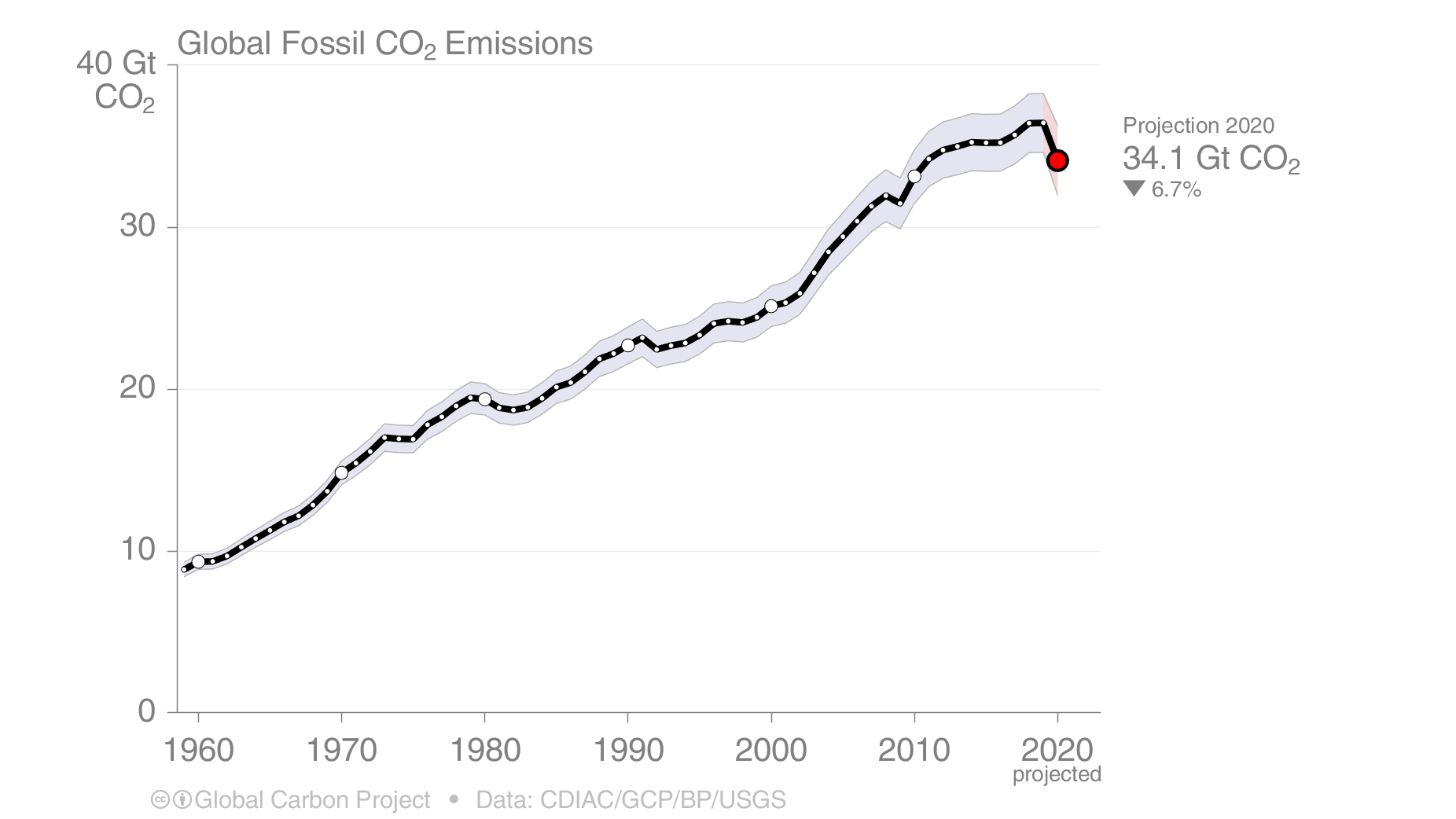
Global Carbon Project Coronavirus Causes Record Fall In Fossil Fuel Emissions In Carbon Brief
26 March 18 UK greenhouse gas emissions final figures xlsx and ods data tables updated New annex added final emissions by end user and fuel type 4 February First Reductions on this scale would be even larger than 's drop in emissions That 64% dip occurred only because many parts of the world came to a forced standstill because of COVID19 Without Greenhouse Gas Inventory Experts Upbeat on Achievements UN Climate Change News, 9 February 21 Experts from around the world who annually review information submitted by developed countries on their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and removals celebrated the year anniversary of the important transparency process last year, while



Earthcharts Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector



Greenhouse Gas Emissions World Energy Data
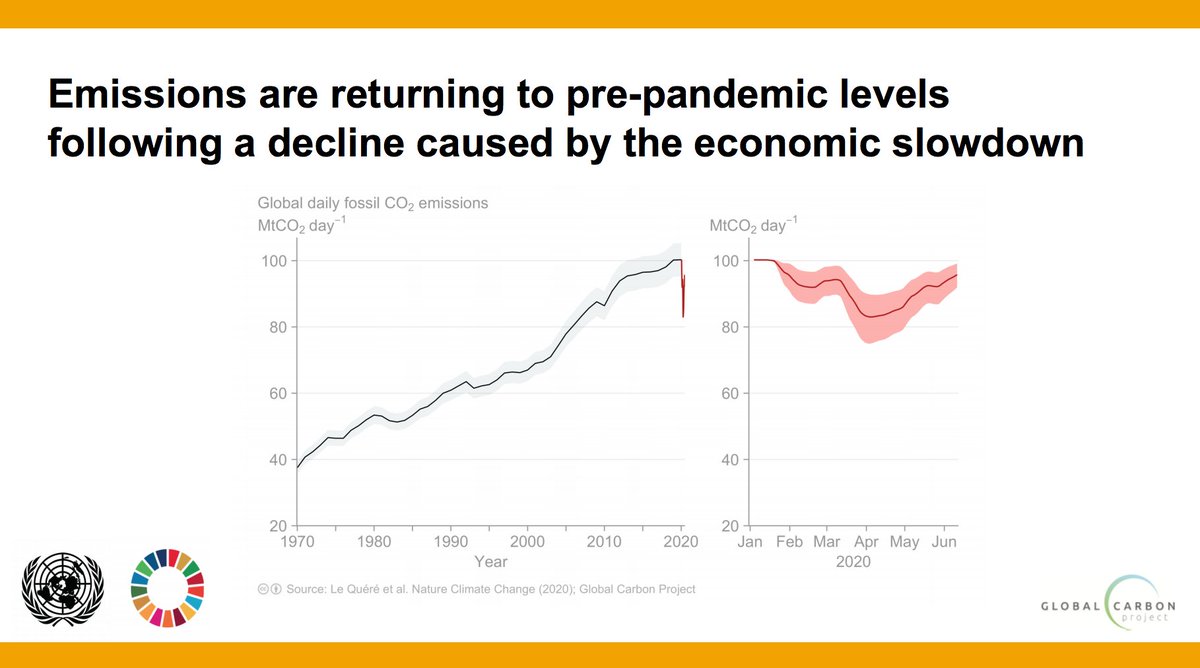
What trajectories of future emissions look like; Greenhouse gas emissions almost back at preCOVID level In Q2 21, greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions showed a yearonyear increase of 11 percent This means emissions are nearing preCOVID levels The increase is mainly due to higher natural gas consumption, for heating and higher manufacturing output among other thingsNot only are annual emissions in set to decline at an unprecedented rate, the decline is set to be almost twice as large as all previous declines since the end of World War II combined Global CO 2 emissions were over 5% lower in Q1 than in Q1 19, mainly due to a 8% decline in emissions from coal, 45% from oil and 23% from natural gas CO 2 emissions fell more than




Global Co2 Emissions To Drop 4 7 In But Will It Matter




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
Greenhouse gases emissions in the EU and in the world The charts above list EU countries by total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 17 and the infographic below shows the world's top greenhouse gas emitters in 15 The EU is the third biggest emitter behind China and the United State and followed by India and RussiaThe EU has set itself targets for reducing its greenhouse gas emissions progressively The EU is on track to meet the % emissions reduction target for By 50, Europe aims to become the world's first climateneutral continent The aim of Mission is to bring "new urgency" to the "global climate conversation" with a call to begin "rapidly declining" global greenhouse gas emissions by Today, in a coauthored commentary published in the journal Nature, Figueres sets out further details about Mission 's six central calls to action



Cait Climate Data Explorer




Climate Change How Quickly Are We Emissions Reducing World Economic Forum
In 19, net greenhouse gas emissions in the United Kingdom (UK) were 4548 million tonnes carbon dioxide equivalent (CO 2 e), of which 80% was carbon dioxide (CO 2) UK cumulative emissions are about 3% of the world total Emissions decreased in the 10s due to the closure of almost all coalfired power stations, but in 18 emissions per person were around 7 tonnes, stillWhere our emissions come from;The emissions in the World Resources Institute's Climate Watch Country Historical Greenhouse Gas Emissions dataset as of December may reflect revisions of data previously published by that organization The emissions reported by the World Resources Institute are also slightly different from the emissions reported by member countries in their National Inventory Report to




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Fossil Co2 Emissions In The Post Covid 19 Era Nature Climate Change
(May ) This is a list of countries by total greenhouse gas (GHG) annual emissions in 16 It is based on data for carbon dioxide, methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) emissions compiled by the World Resources Institute (WRI) The table below separately provides emissions data calculated on theThe update provides estimates of Australia's national inventory of greenhouse gas emissions up to the September quarter of Emissions were 5101 million tonnes – 44% or 233 million tonnes lower than in 19 They were 19 % below the level of emissions in 05 (the baseline year for the Paris Agreement) Greenhouse gas measurement data are archived and distributed by the World Data Centre for Greenhouse Gases (WDCGG) at the Japan Meteorological Agency which celebrates its 30th anniversary in
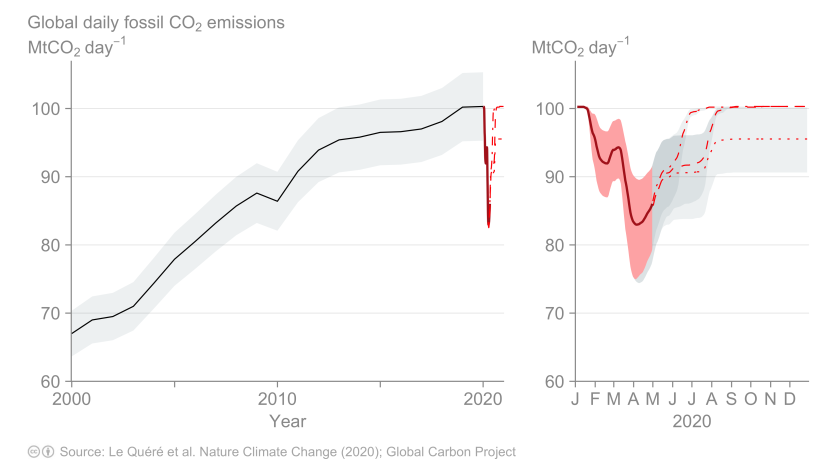



Coronavirus Crisis Leads To 17 Drop In Global Carbon Emissions Los Angeles Times
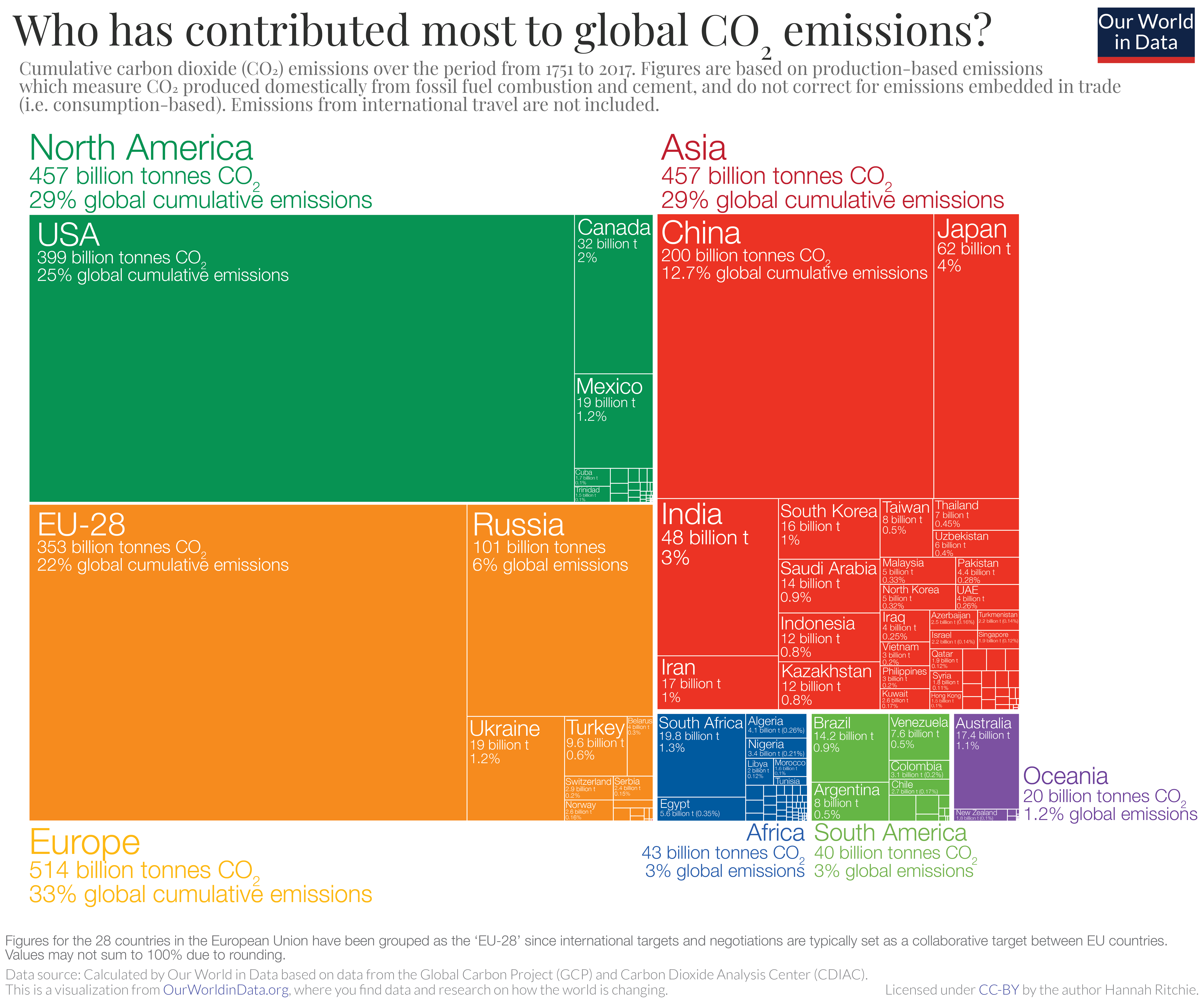



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
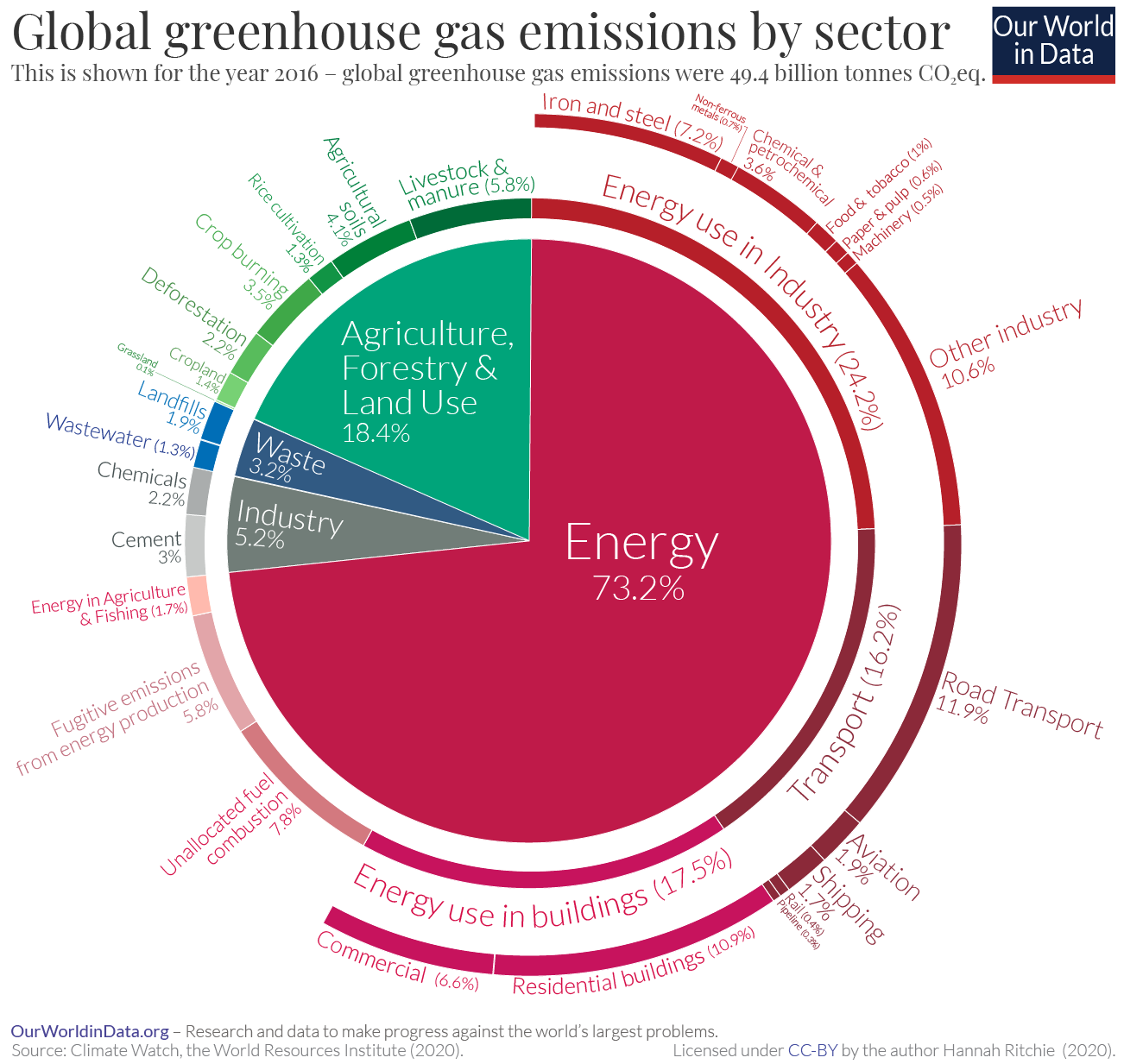
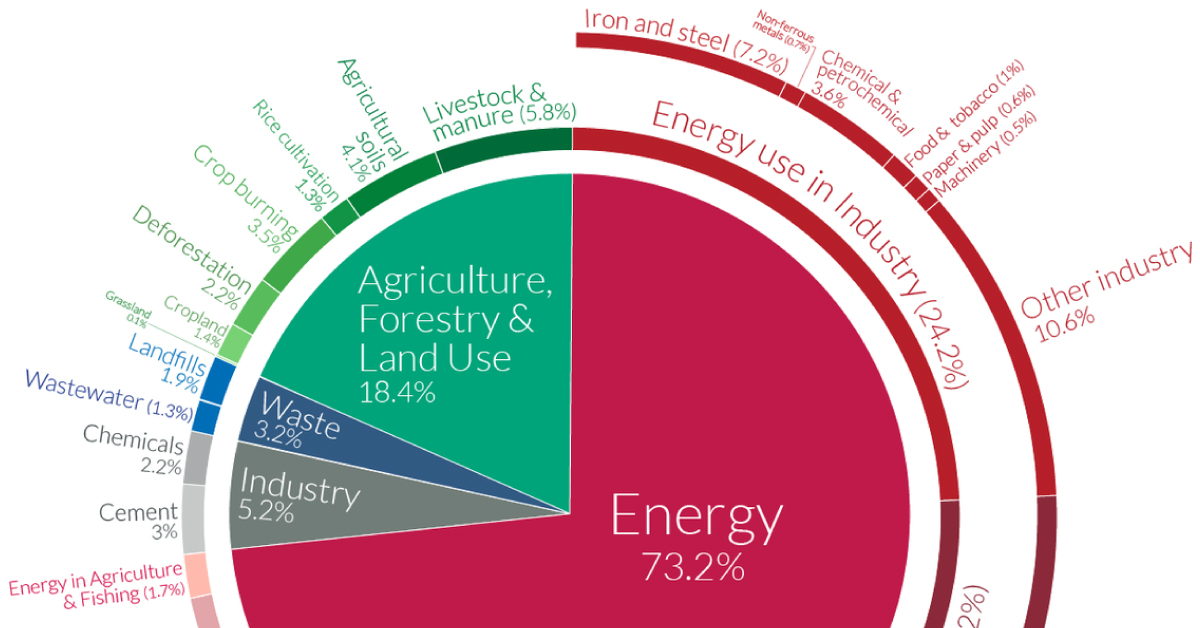
This figure shows worldwide greenhouse gas emissions by sector from 1990 to 15 For consistency, emissions are expressed in million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalents These totals include emissions and sinks due to landuse change and forestry Note that the sectors shown here are different from the economic sectors used in US emissions accountingEmissions decline can now be made The finer disaggregation of world regions in the WWFUKMIRO model allows for new insights into the origin of the UK's carbon footprint MAIN RESULTS Between 1990 and 16 the UK reported a 41% reduction in greenhouse gas emissionsIn 18 New Zealand's gross greenhouse gas emissions were 7 million tonnes of CO 2 e, 240 percent higher than 1990 and 10 percent lower than 17 Gross GHG emissions were mainly made up of carbon dioxide (445 percent), methane (435 percent), and nitrous oxide (96 percent)
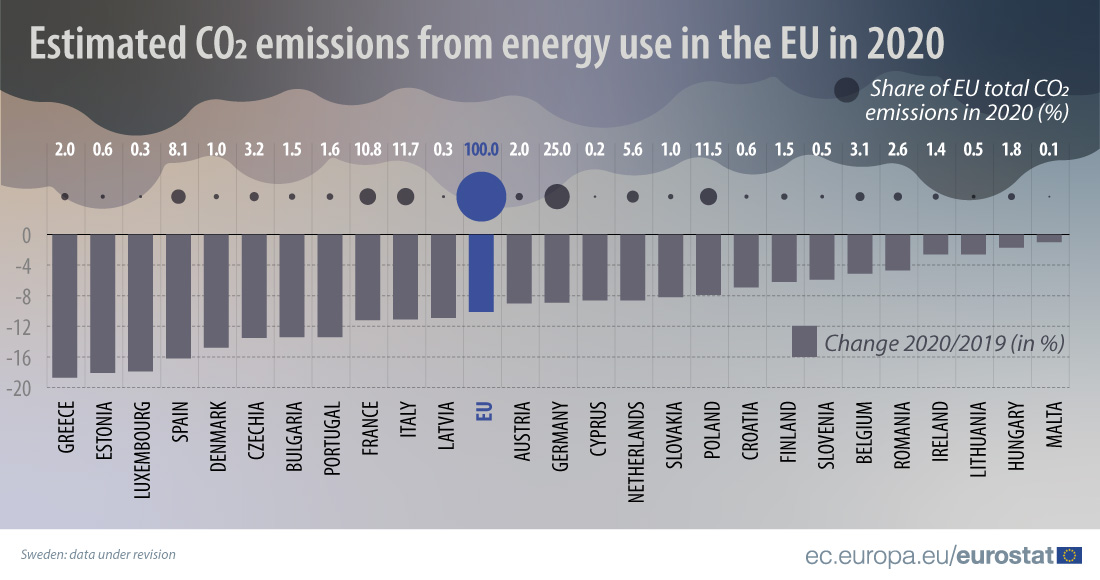



Co2 Emissions From Energy Use Clearly Decreased In The Eu In Products Eurostat News Eurostat
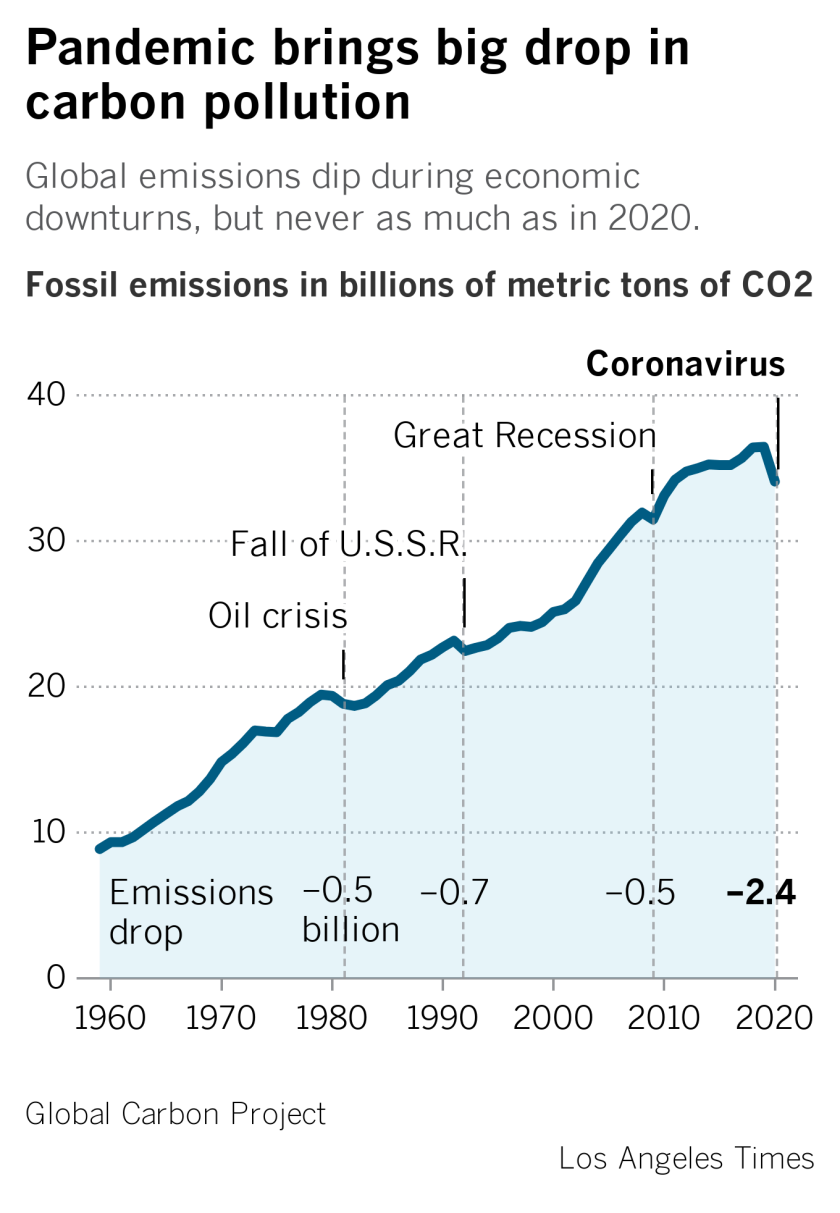



Global Carbon Emissions Dropped 7 Amid Covid 19 Los Angeles Times
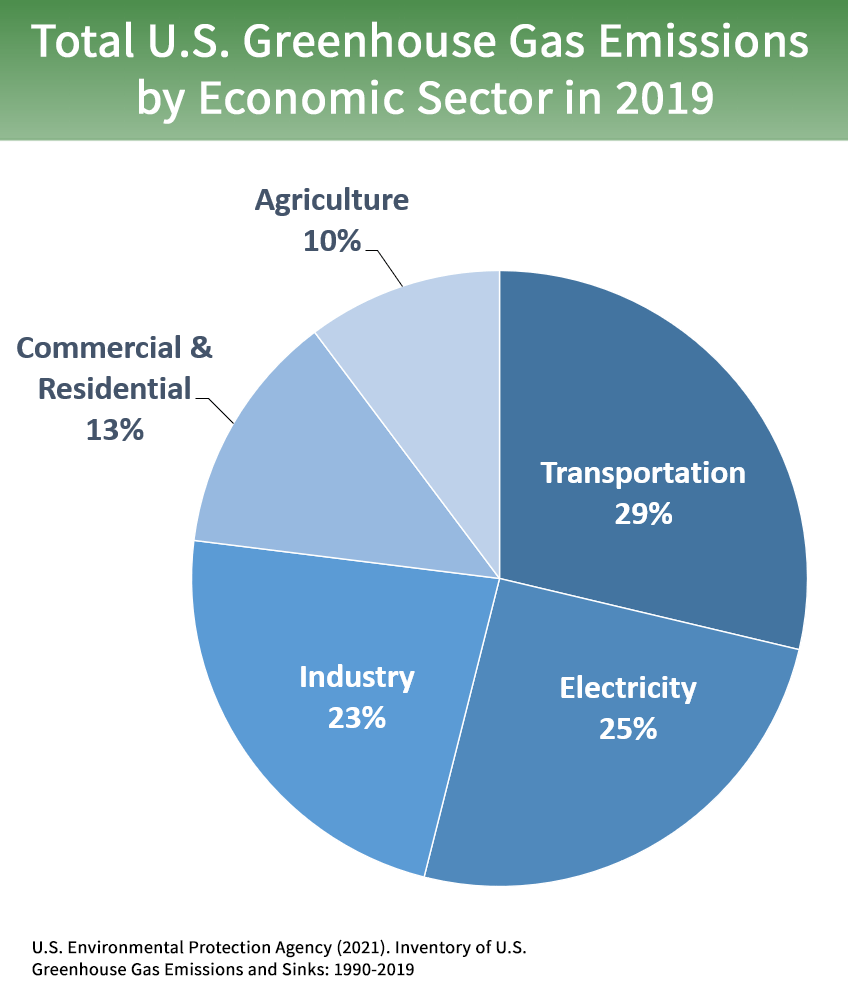
UK greenhouse gas emissions, provisional figures 25 March 21 National Statistics In the coronavirus (COVID19) pandemic and the resulting restrictions brought in across the UK had a major impact on various aspects of society and the economy and this has had a significant impact on greenhouse gas emissions in the UK over this period • Carbon dioxide (CO 2) As defined by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), US greenhouse gas emissions sources can be broken down into five sectors transportation (29%), electricity (28%), industry (22%), commercial and residential (12%), and agriculture (9%) Transportation is currently the largest source of greenhouse gas emissions in the US, having surpassed electricity The Global Energy Review's projections of energy demand and energyrelated emissions for are based on assumptions that the lockdowns implemented around the world in response to the pandemic




Eia Projects Global Energy Related Co2 Emissions Will Increase Through 50 Today In Energy U S Energy Information Administration Eia



Carbon Emissions Energy Economics Home
Indeed, global energyrelated carbon emissions fell by 58% in , or nearly 2 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide, thanks to reduced demand for oil, coal and gas Such a reduction, alone, would have Transport already represents a quarter of energyrelated greenhouse gas emissions—a figure that could increase to 33% under a businessasusual scenario The scale of the problem is made evident by the stark contrast in many cities' air quality from before and during the COVID19 urban transport slowdown Like pollution, GHG emissions dropped significantly inTo prevent severe climate change we need to rapidly reduce global greenhouse gas emissions The world emits around 50 billion tonnes of greenhouse gases each year measured in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 eq) 1 To figure out how we can most effectively reduce emissions and what emissions can and can't be eliminated with current technologies, we need to first




Co2 Emissions From Fossil Fuels May Have The Breakthrough Institute



News Global Ghg Emissions Reached New High In 19
The decline in CO2 emissions from oil use in the transport sector accounted for well over 50% of the total global drop in CO2 emissions in , with restrictions on movement at local and international levels leading to a near 1 100 Mt drop in emissions from the sector, down almost 14% from 19 levels With various travel advisories and border restrictions, international1 day ago Last year, greenhouse gas emissions in South Korea amounted to 6486 million tonnes, a 73% decrease compared to 19 Climate change Global greenhouse gas levels were highest ever in despite lockdowns, study finds Lockdowns in the COVID19 pandemic did little to curtail greenhouse gas buildups and Europe



Data Supplement To The Global Carbon Budget Icos
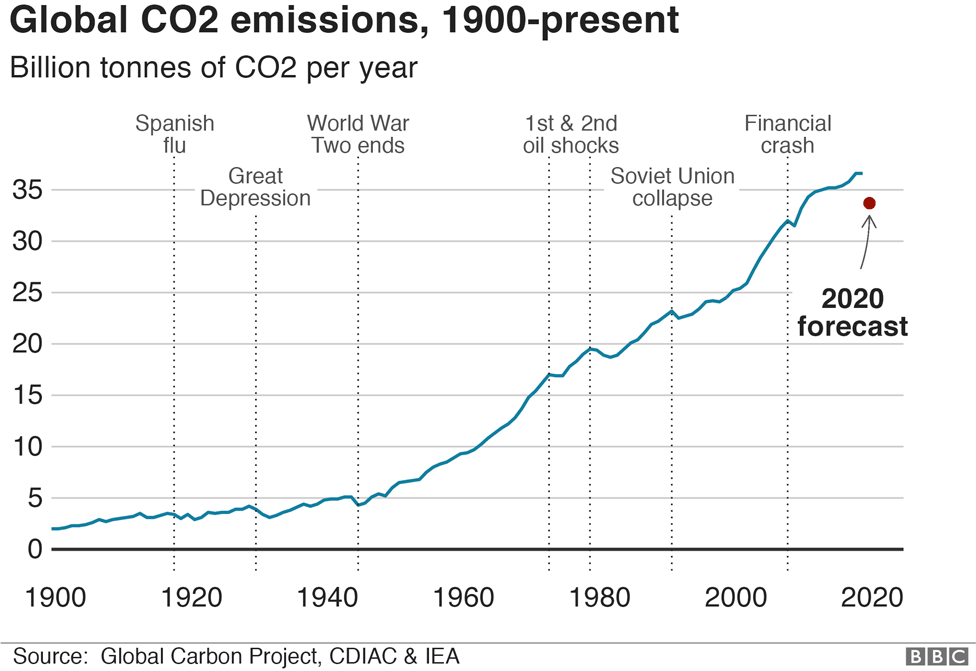



Climate Change And Coronavirus Five Charts About The Biggest Carbon Crash c News
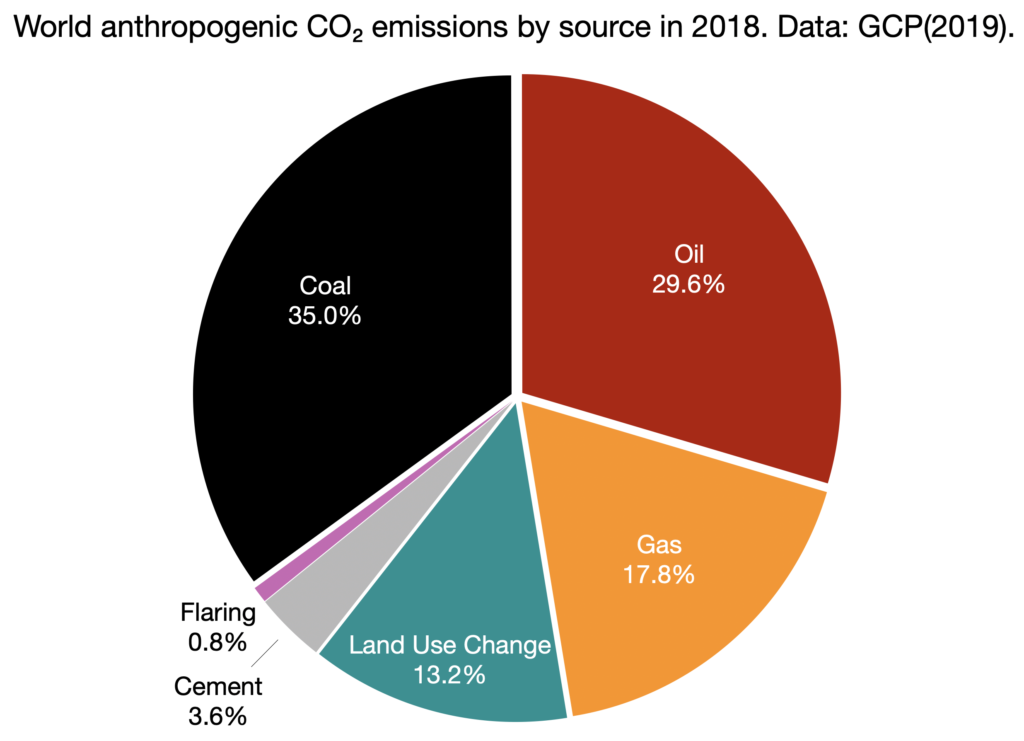
Greenhouse gas emissions could increase from 55 gigatons of CO2 equivalents (GtCO2e) in 19 to over 80 GtCO2e in 50 an almost 50 percent increase Causes of CO2emissions CO2emissions are mostly a result of burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas In 18, emission of CO2 from fossil fuels were Coal 147 billion tons



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
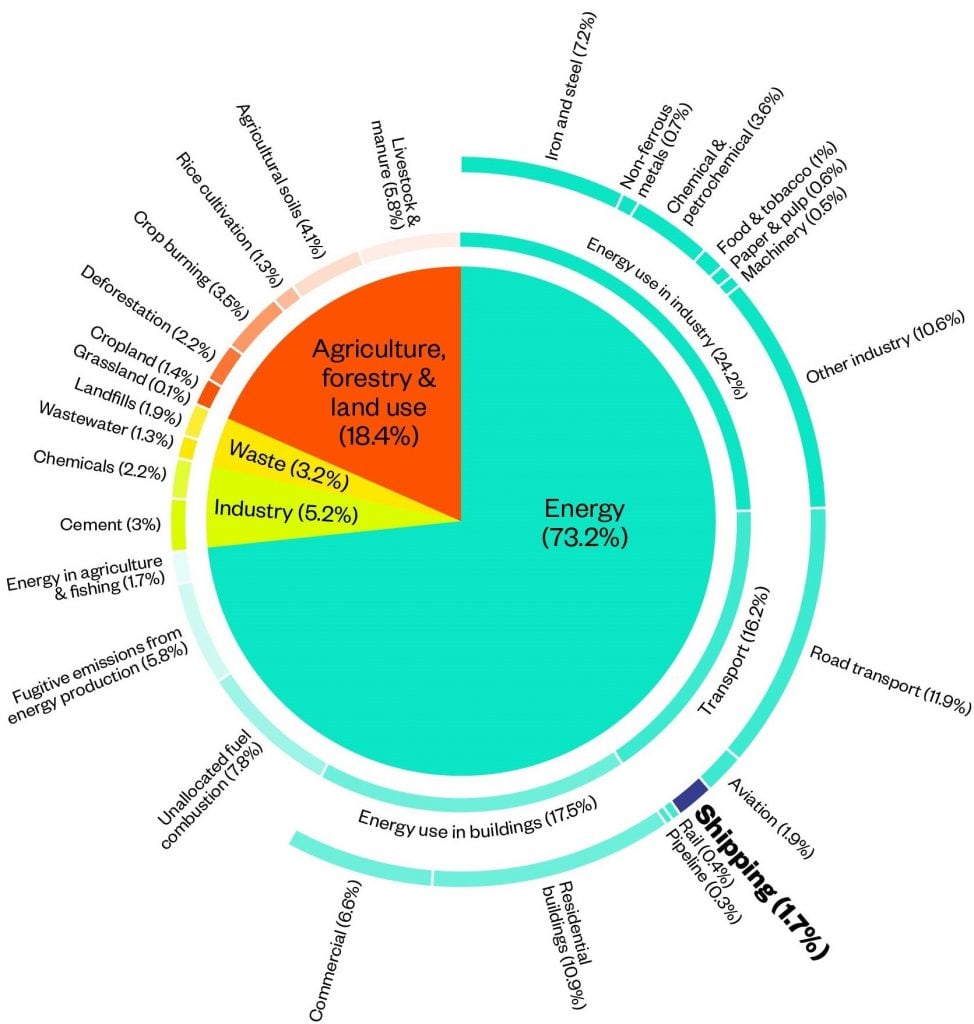



Environmental Initiatives International Chamber Of Shipping
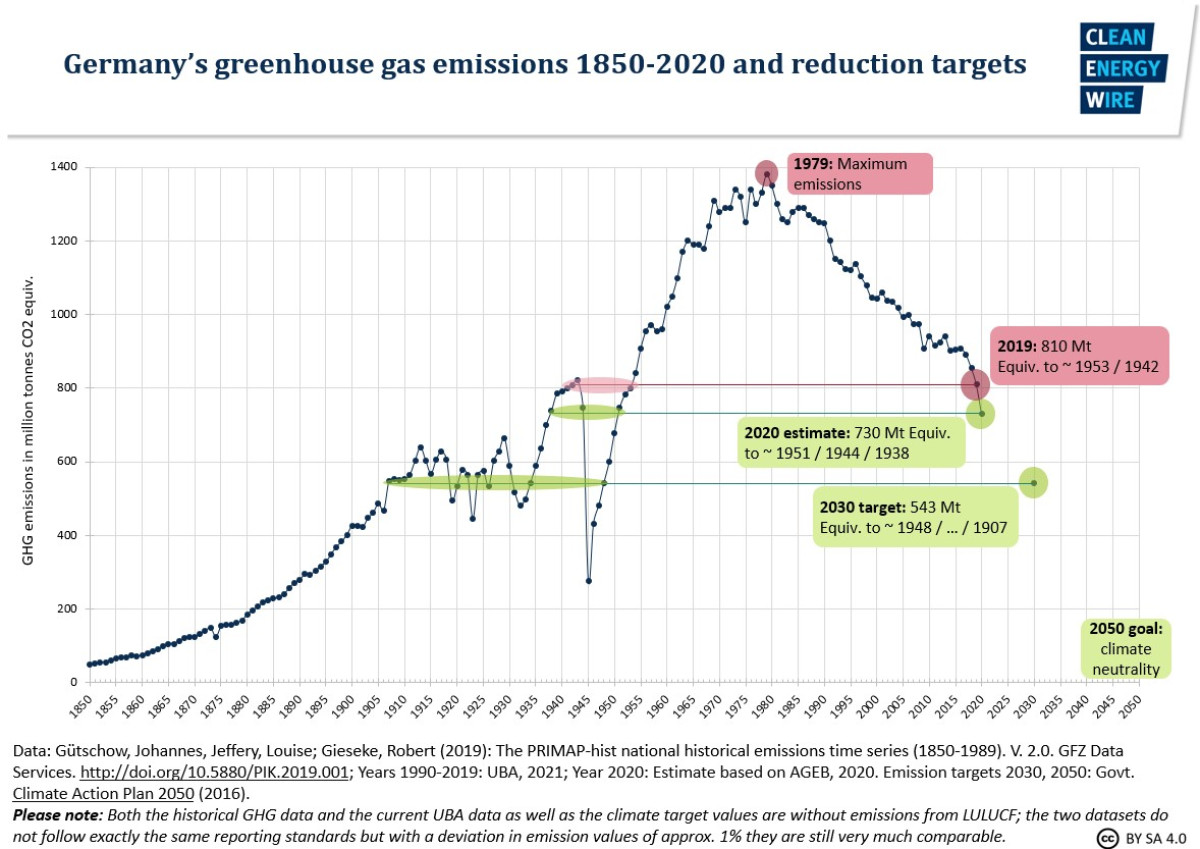



Germany S Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Energy Transition Targets Clean Energy Wire




Daily Global Co2 Emissions Cut To 06 Levels During Height Of Coronavirus Crisis World Economic Forum
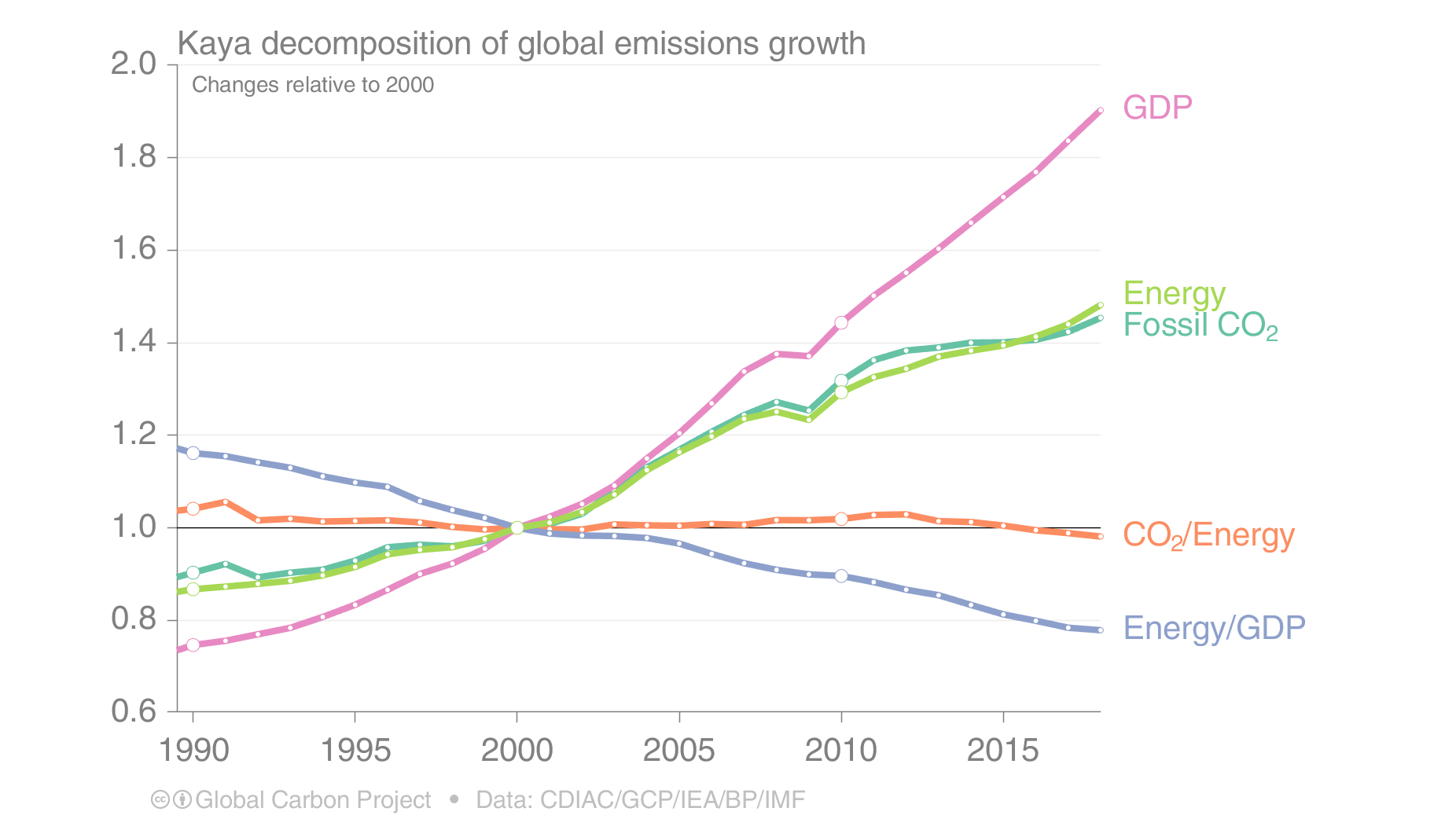



Here S How Much Global Carbon Emission Increased This Year Ars Technica




Uk And Global Emissions And Temperature Trends




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research




File Global Human Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector 16 Png Wikipedia
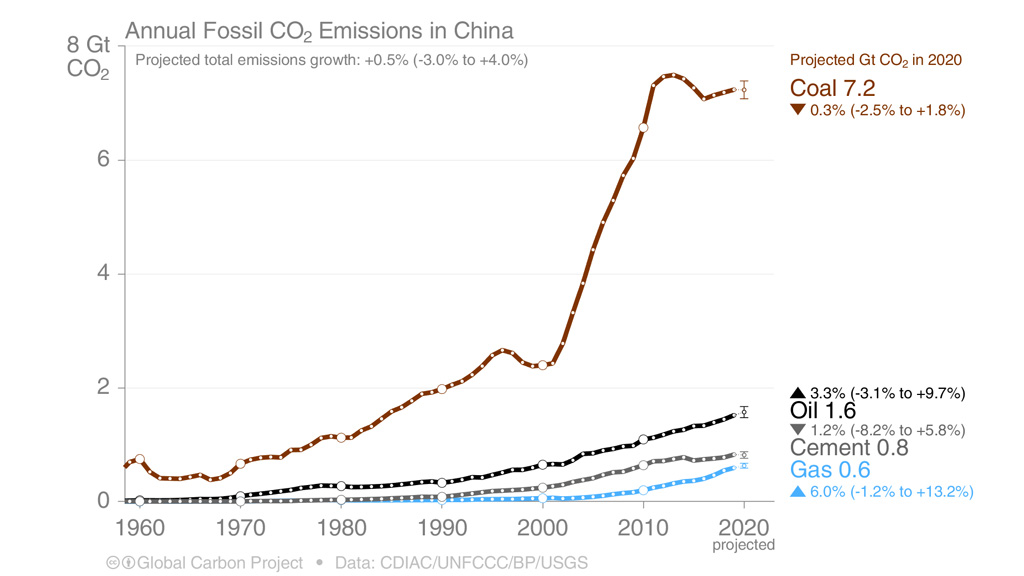



Global Carbon Project Coronavirus Causes Record Fall In Fossil Fuel Emissions In Carbon Brief
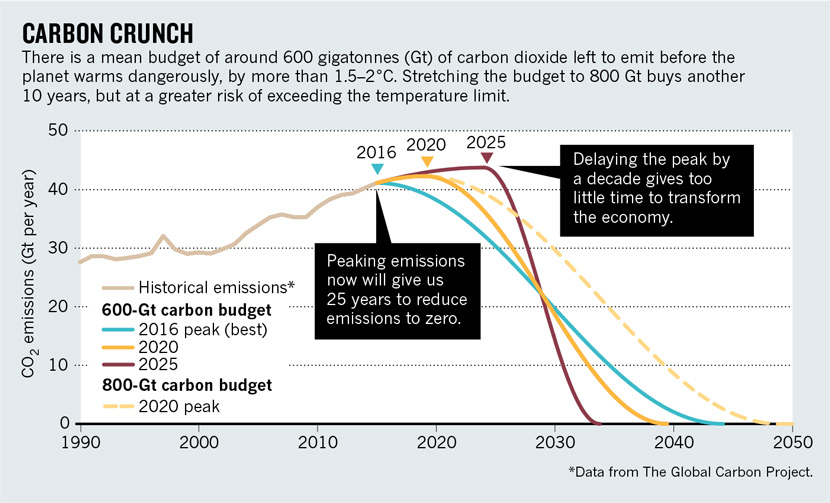



Mission A New Global Strategy To Rapidly Reduce Carbon Emissions Carbon Brief




Emissions Are Surging Back As Countries And States Reopen The New York Times



1




Gcp Carbon Budget
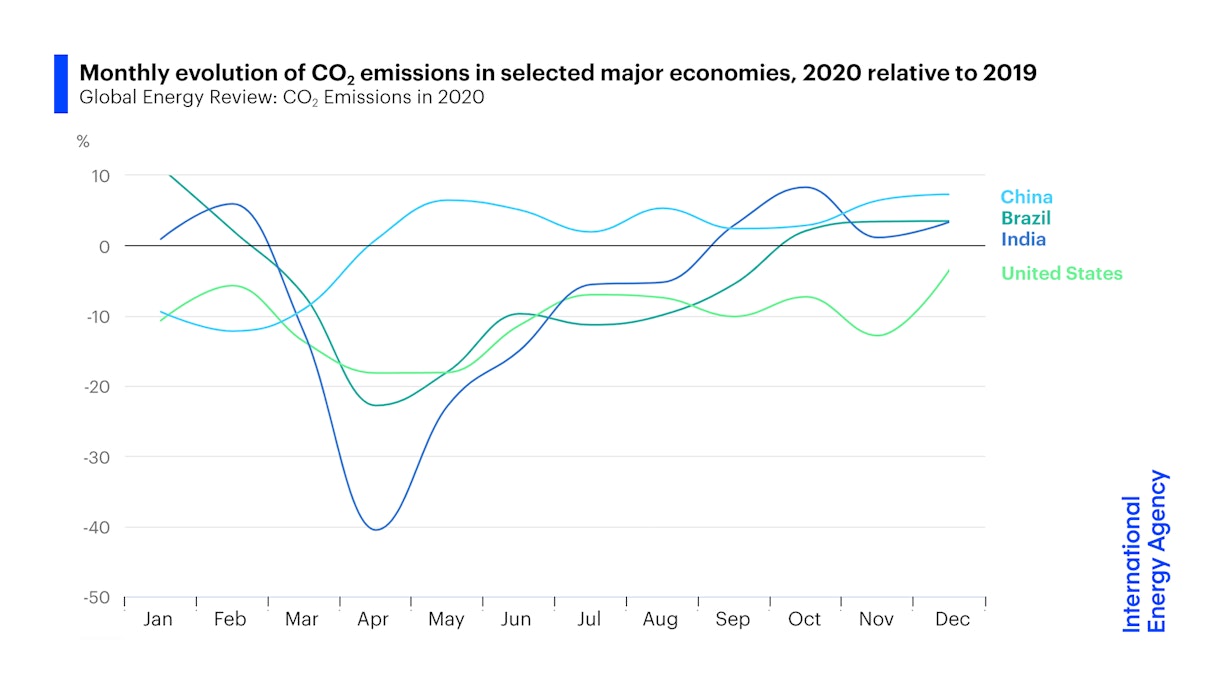



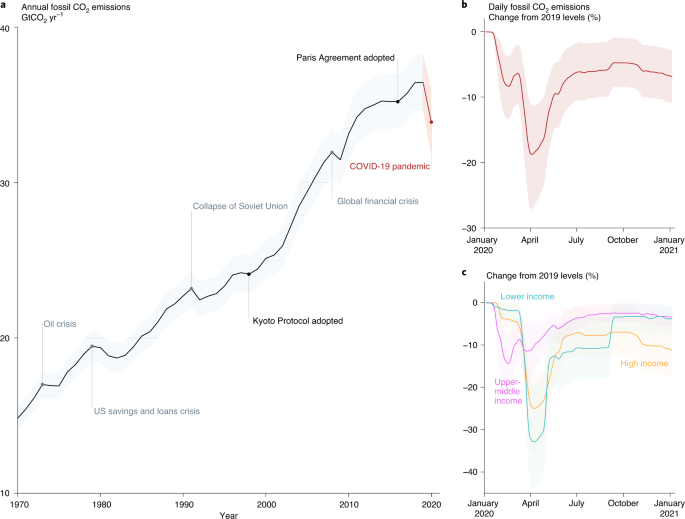
After Steep Drop In Early Global Carbon Dioxide Emissions Have Rebounded Strongly News Iea



Print Page
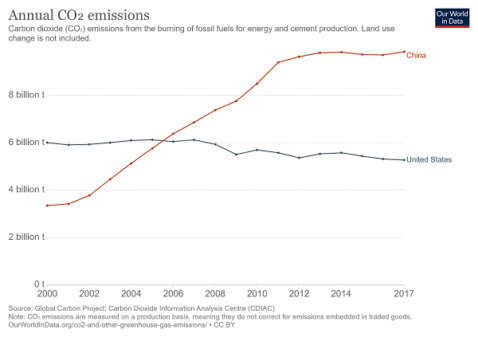



Where Are Us Emissions After Four Years Of President Trump



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector 10 Total Emissions Were Download Scientific Diagram



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data



Total Greenhouse Gas Emission Trends And Projections In Europe European Environment Agency
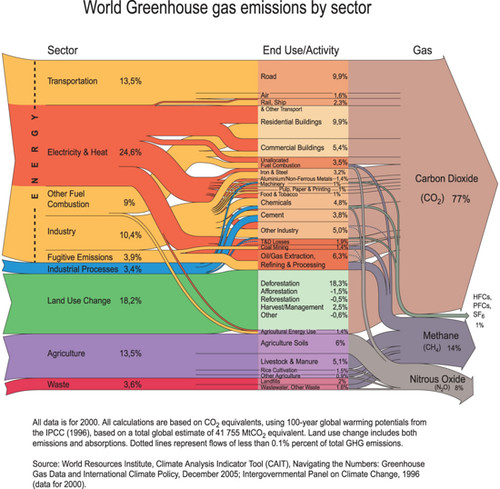



World Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector Grid Arendal
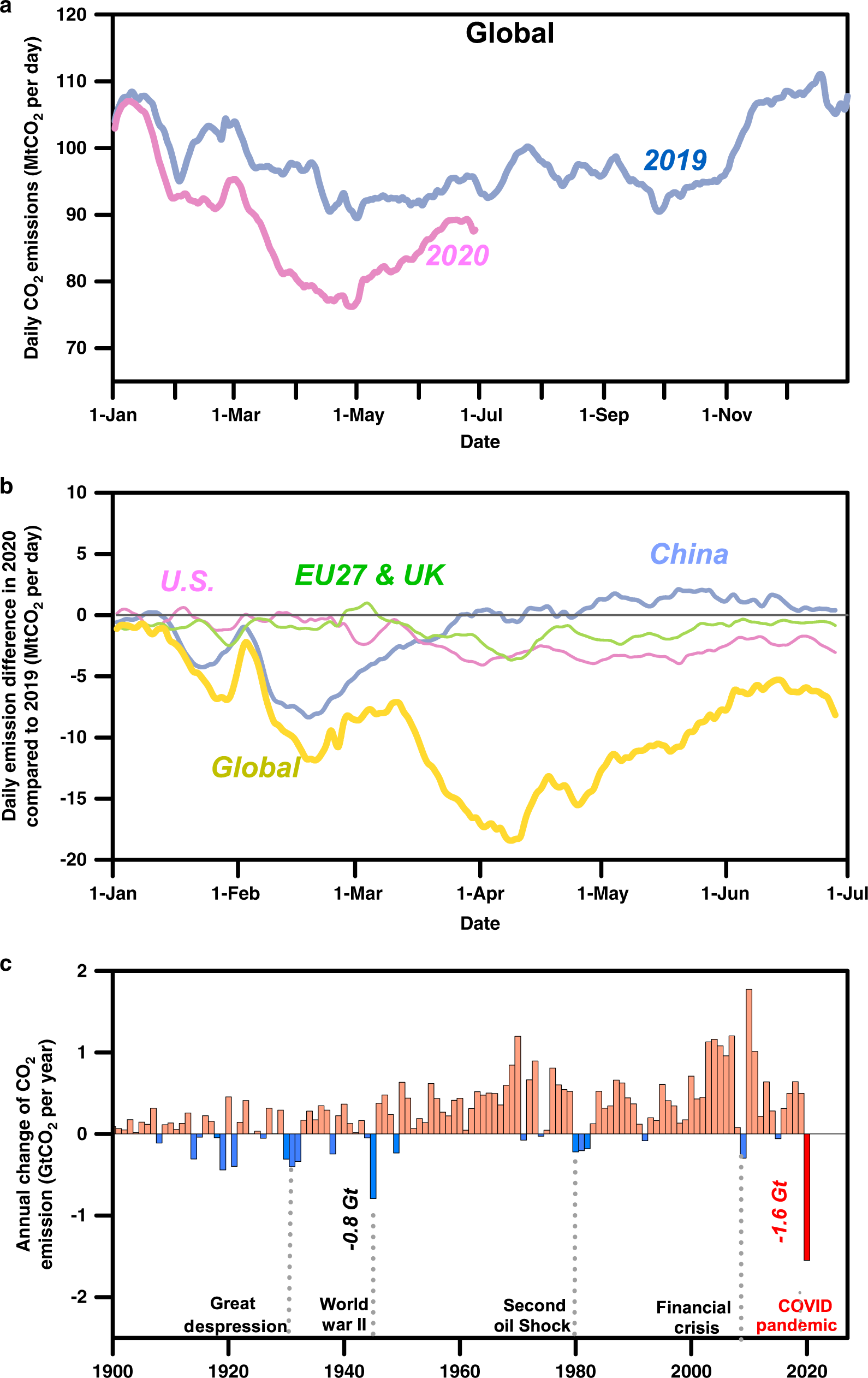



Near Real Time Monitoring Of Global Co2 Emissions Reveals The Effects Of The Covid 19 Pandemic Nature Communications



2
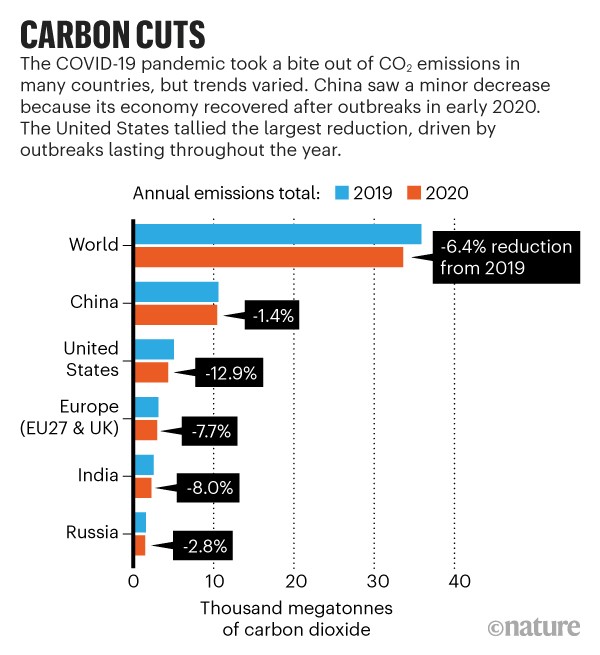



Covid Curbed Carbon Emissions In But Not By Much




Chart Global Carbon Emissions Fall In Statista



File Annual Greenhouse Gas Emissions Owid Svg Wikimedia Commons



2




Sector By Sector Where Do Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Our World In Data




Share Of Global Co2 Emissions By Sector Statista




Got Beef Here S What Your Hamburger Is Doing To The Climate




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization



1
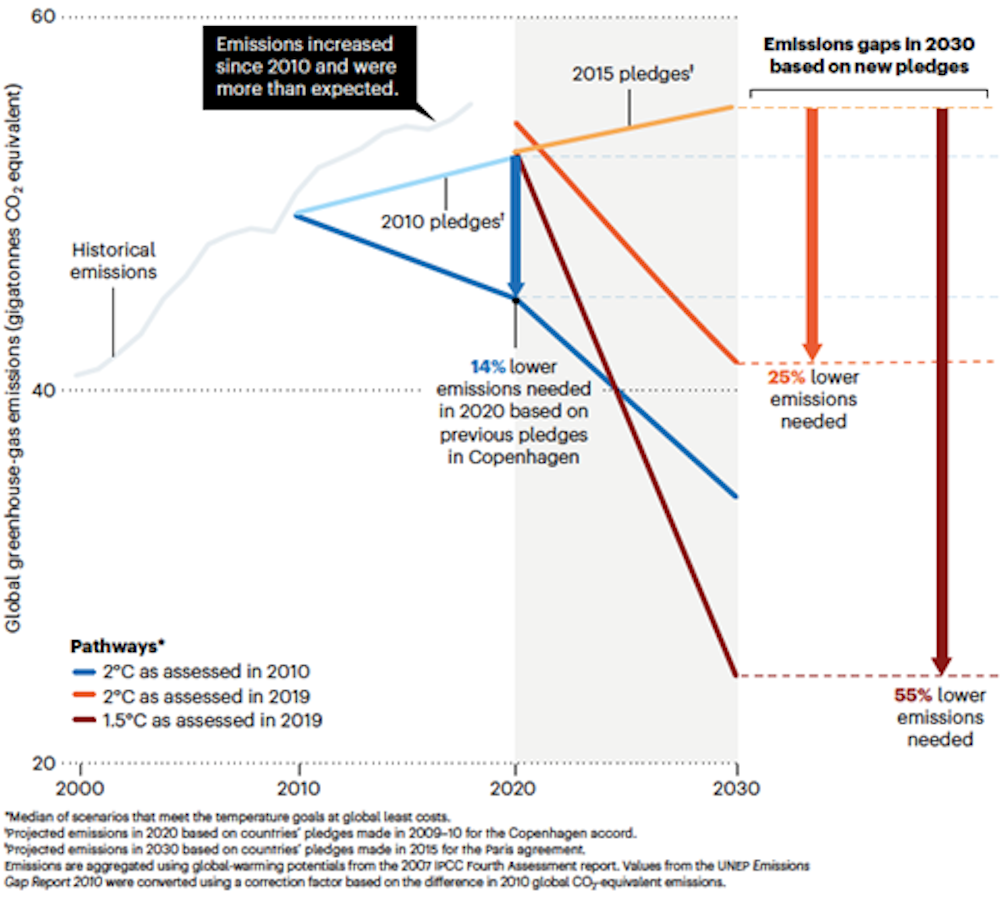



Global Emissions Are Way Off Target What Needs To Happen




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa




Seedquest Central Information Website For The Global Seed Industry




Covid 19 Lockdowns Behind Record Drop In Global Co2 Emissions Gcp Bioenergy International
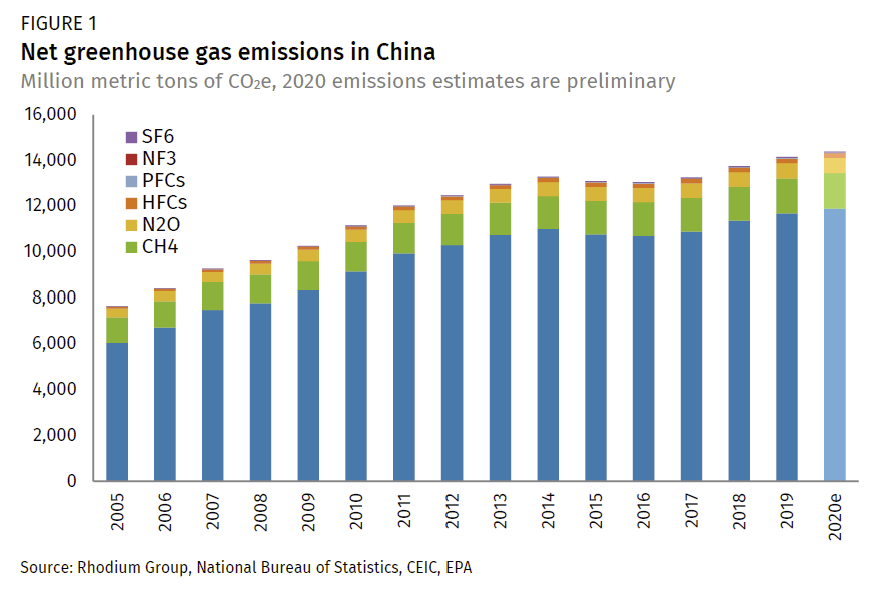



Preliminary Greenhouse Gas Emissions Estimates For China Rhodium Group



Global Warming




Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




List Of Countries By Carbon Dioxide Emissions Per Capita Wikipedia




Global Transport Co2 Emissions Breakdown Statista
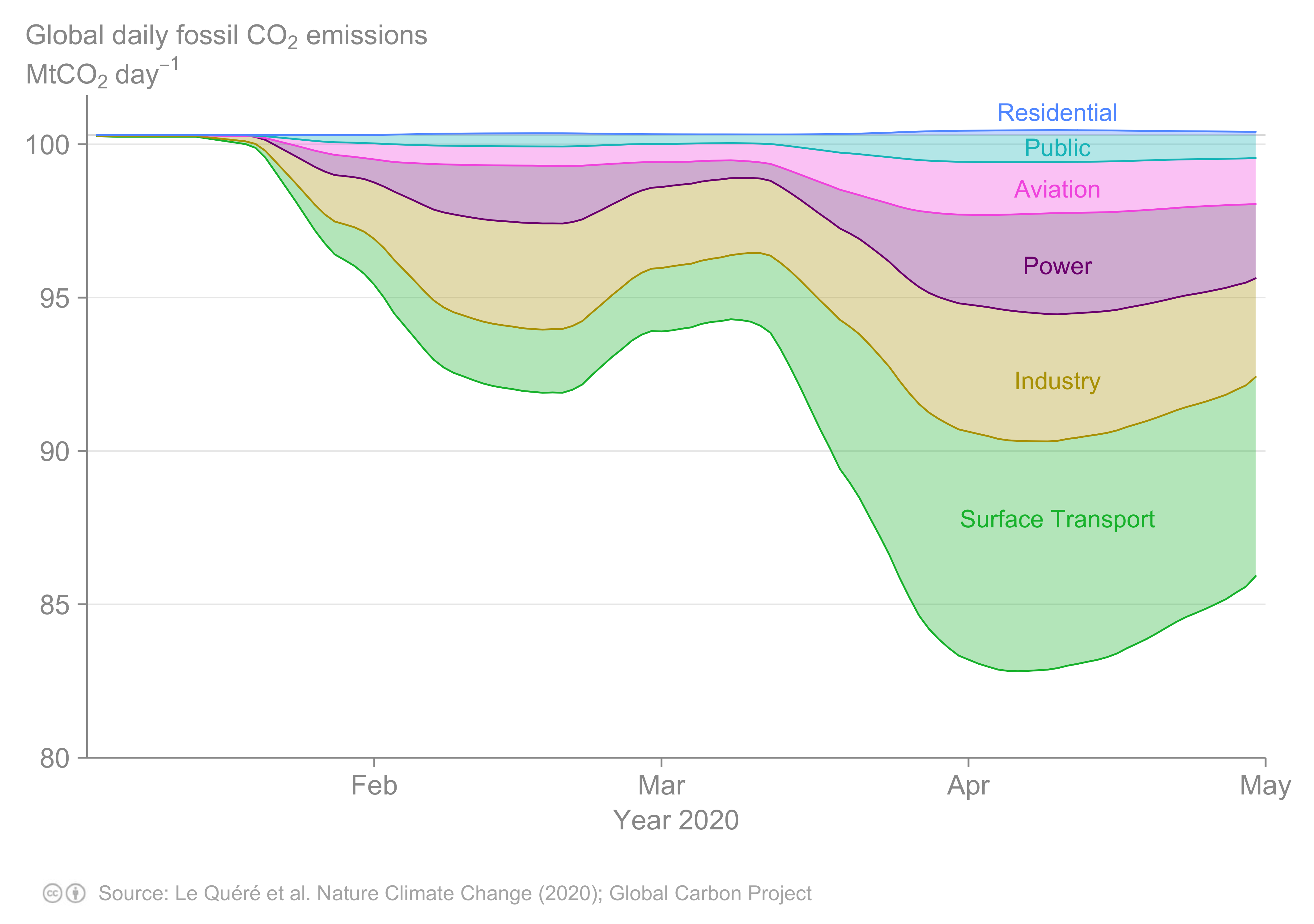



News Temporary Reduction In Daily Global Co2 Emissions During The Covid 19 Forced Confinement
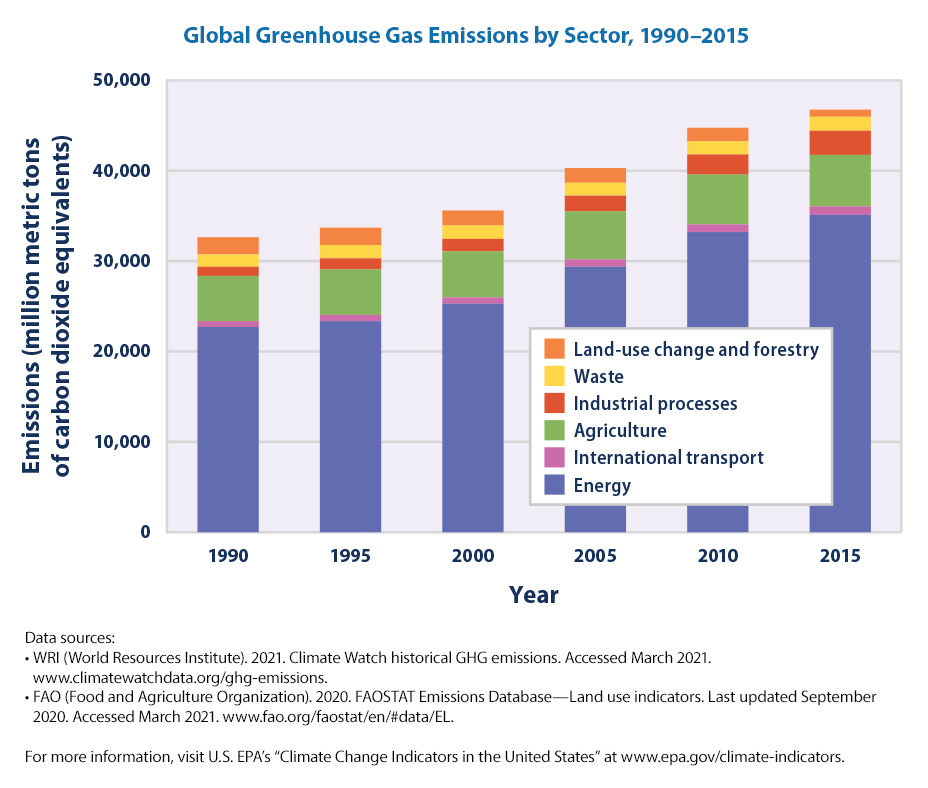



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa




Emissions Gap Report Unep Un Environment Programme




S11 World Greenhouse Gas Emissions 16 Section 3 Reconciling Demand And Supply Context Land Water Food And Climate Civil And Environmental Engineering Mit Opencourseware




File World Greenhouse Gas Emissions 12 World Png Statistics Explained
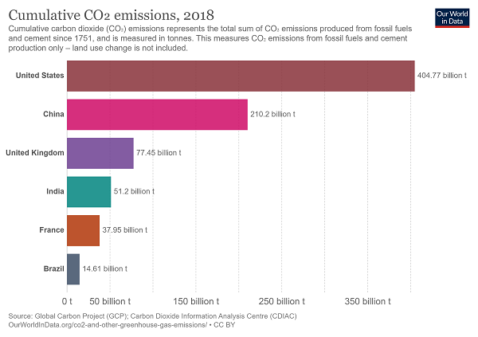



Where Are Us Emissions After Four Years Of President Trump




Emissions Sources Climate Central




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions In The Unmitigated Reference Download Scientific Diagram




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa
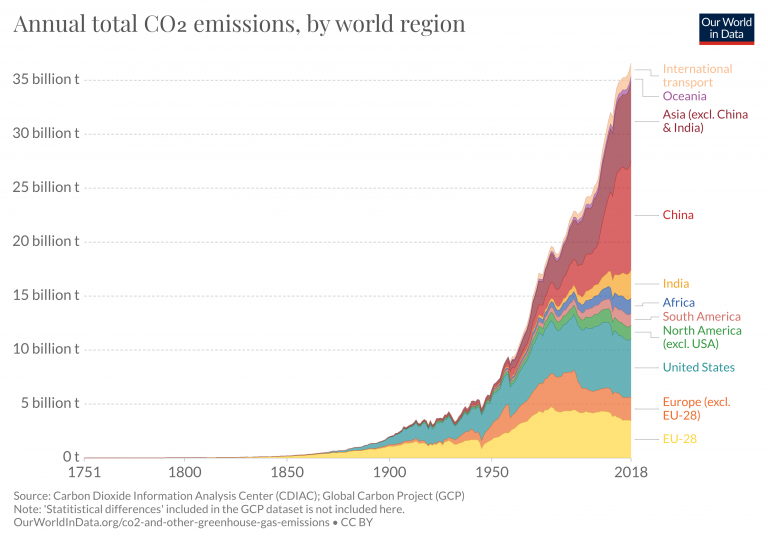



Co2 Emissions Our World In Data
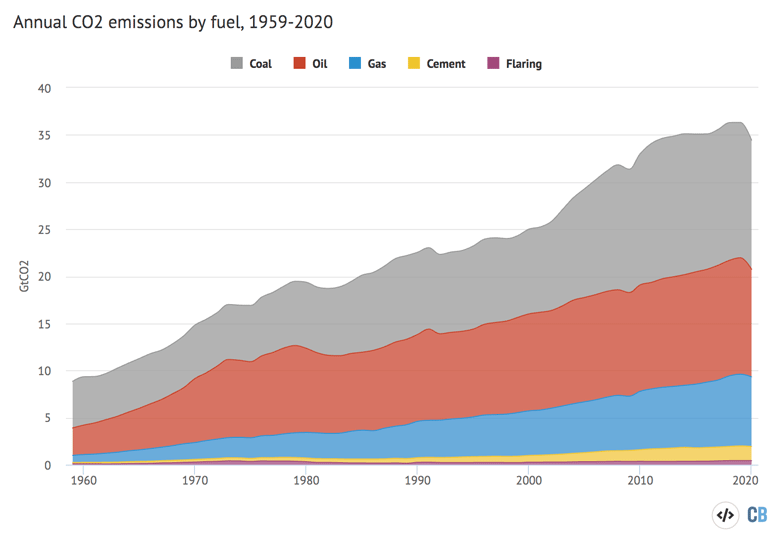



Global Carbon Project Coronavirus Causes Record Fall In Fossil Fuel Emissions In Carbon Brief




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Set To Rise Fast In 21 The Economist
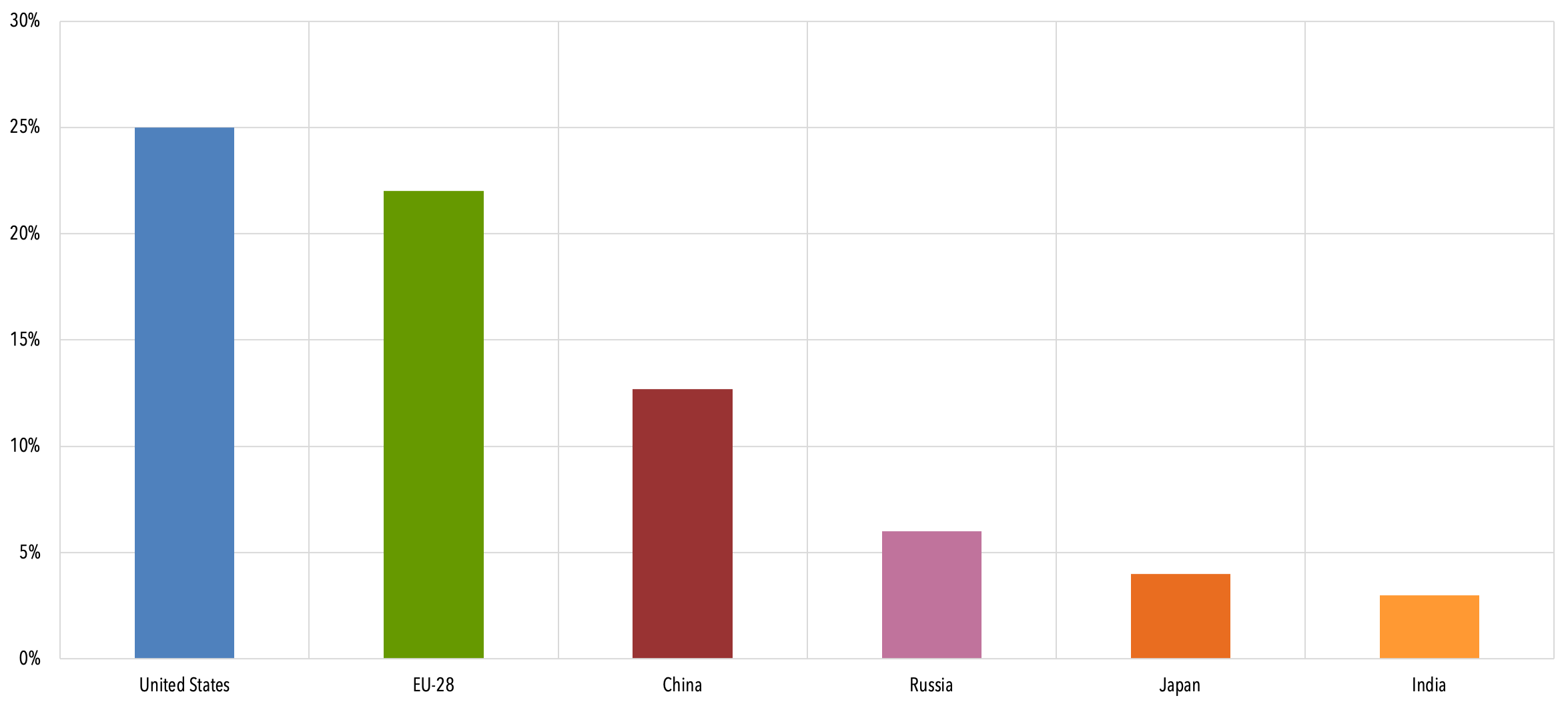



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



Eco Economy Indicators Carbon Emissions Epi




The Shutdown And The Climate Crisis
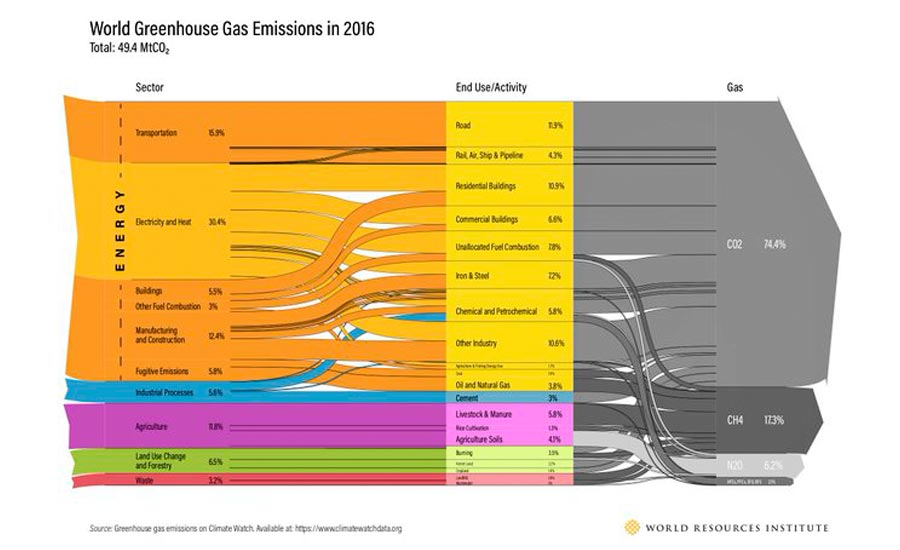



Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Data Is Interactive 02 07 Engineering News Record
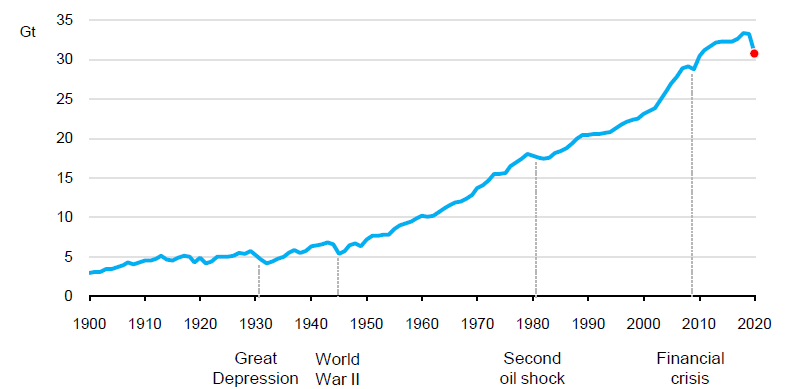



Climate Indicators In The Covid 19 Season Earthzine




France Greenhouse Gas Emissions Decreased By 16 9 From 1990 Levels Climate Scorecard




Highest Greenhouse Gas Emissions In History Push Global Warming Towards Dangerous Levels Global Warming Climate Change Greenhouse Gas Emissions Ghg Emissions
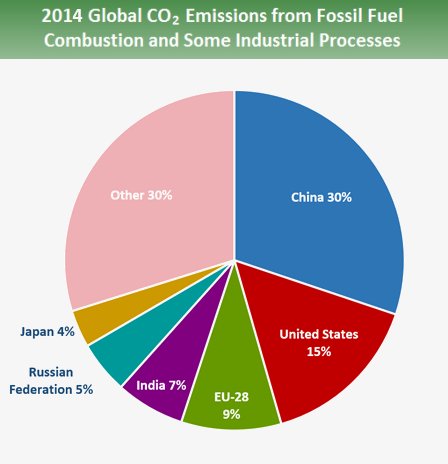



Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



Chart Growing Emissions Which Countries Are To Blame Statista
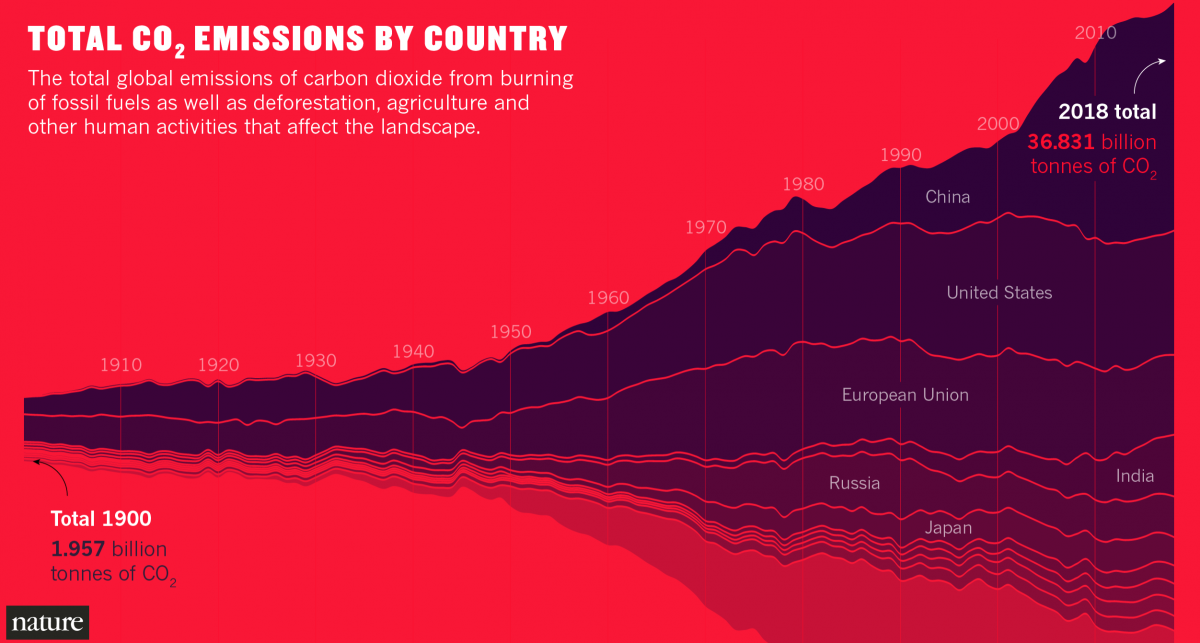



Five Ways Organizations Are Visualizing Carbon Emissions Storybench
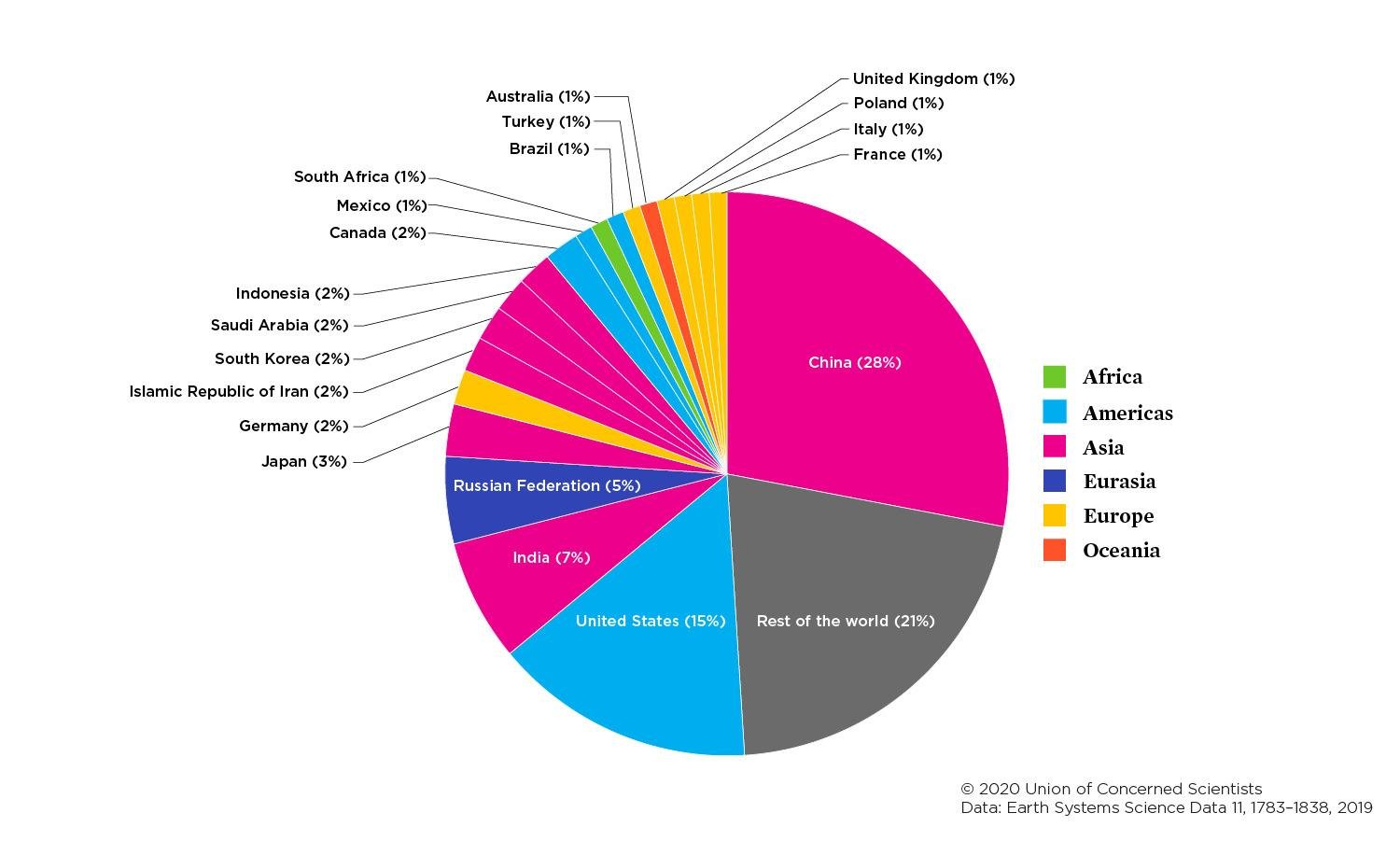



Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
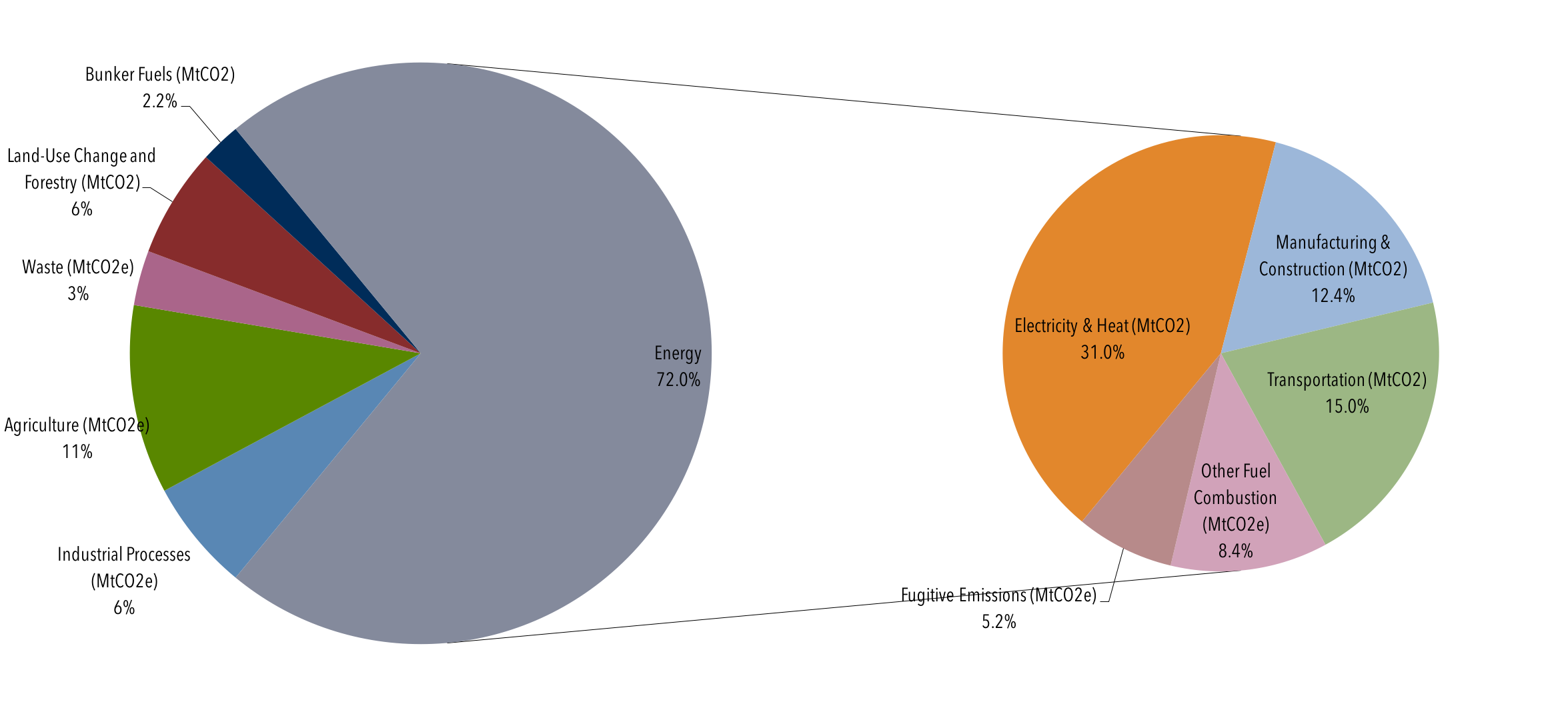



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




After Steep Drop In Early Global Carbon Dioxide Emissions Have Rebounded Strongly News Iea




National And Global Emissions Sources Climate Matters
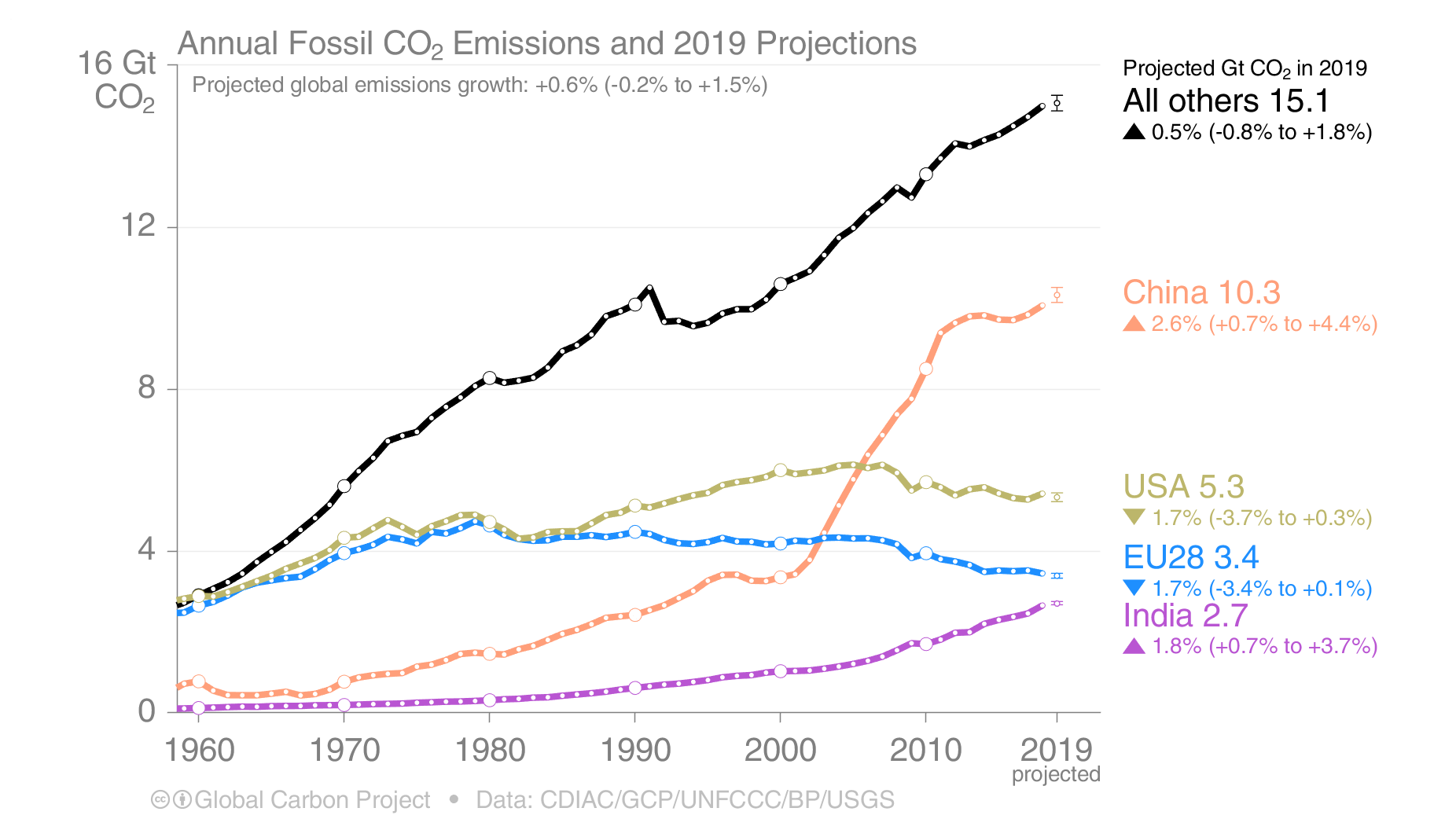



Here S How Much Global Carbon Emission Increased This Year Ars Technica




Pfizer S Progress On Greenhouse Gas Emissions Goals
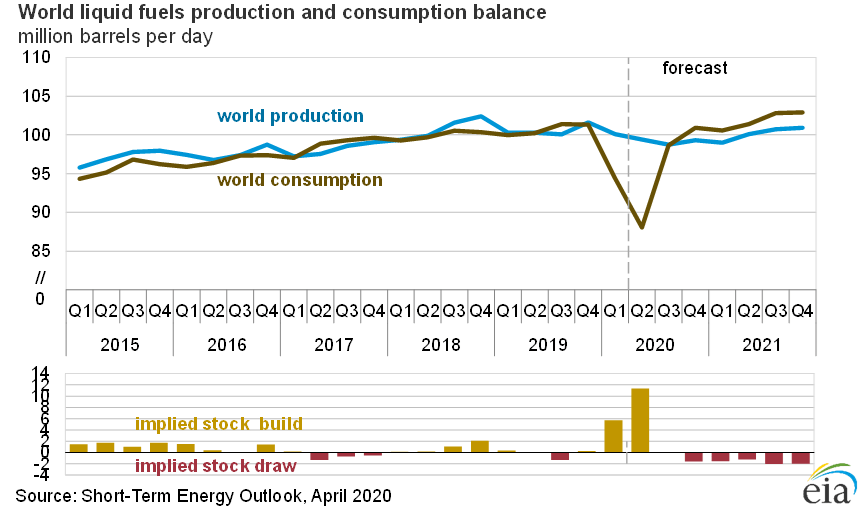



Forecast U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions To Fall 7 5 Percent In Mpr News
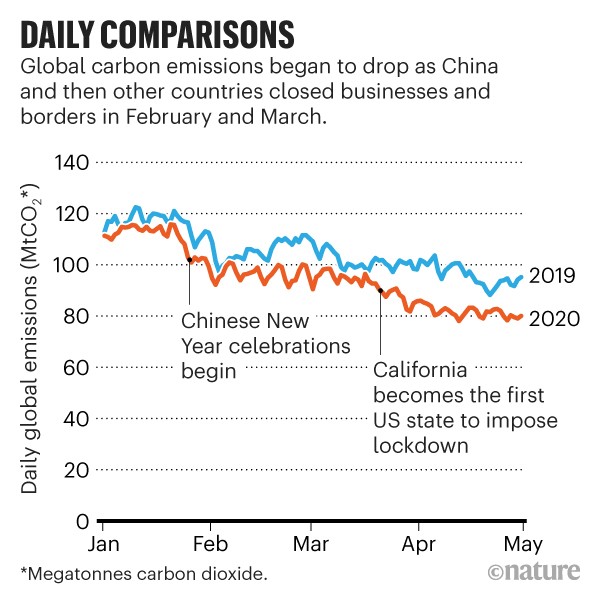



How The Coronavirus Pandemic Slashed Carbon Emissions In Five Graphs
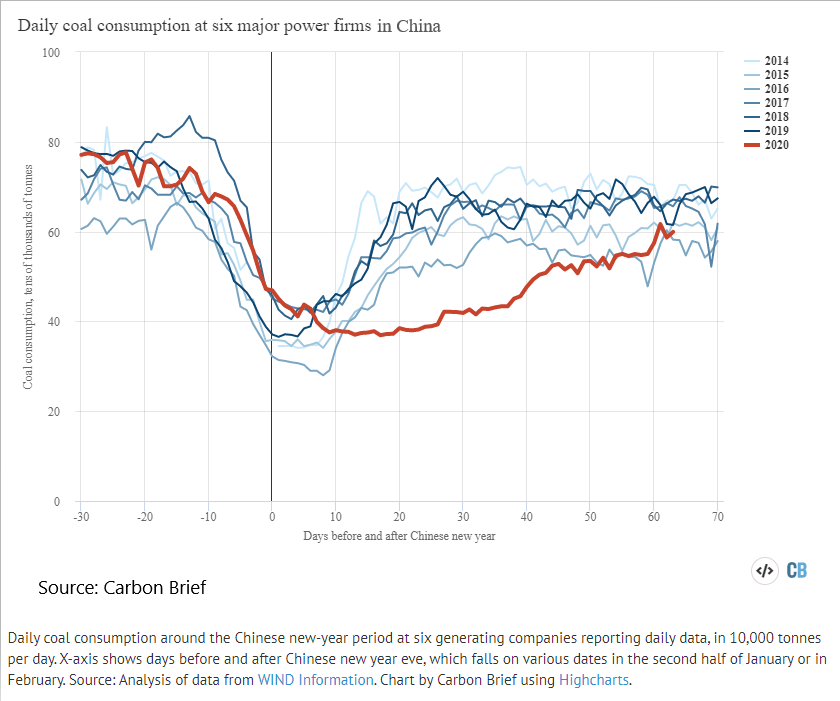



Coronavirus Could Trigger Biggest Fall In Carbon Emissions Since World War Two Reuters




There Is No Climate Silver Lining To The Breakthrough Institute




The Climate Change Performance Index 21 Newclimate Institute




The Effect Of Covid 19 On Co2 Emissions Econofact



World Meteorological Organization A Twitter Unitedinscience Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Already Returning To Pre Covid19 Levels We Need A 4 7 Reduction Every Year In Emissions To Meet Climateaction Targets T Co 7iqwt8t2wm



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿